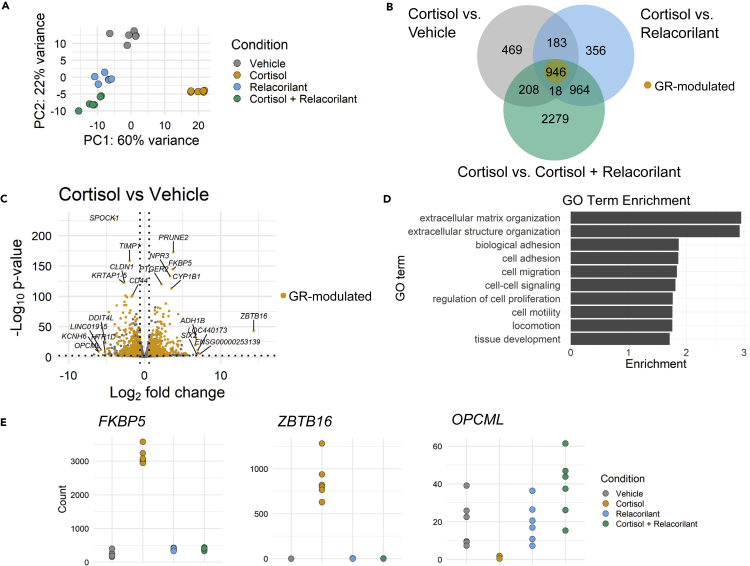
Figure 3.
Chronic stress-driven GR activation modulates mRNA levels of genes with functional roles in fibroblast phenotypes
(A) Principal component analysis (PCA) plot of RNA-seq samples of IMR-90 fibroblasts treated with vehicle (DMSO), cortisol, relacorilant, or cortisol + relacorilant, n = 6 biological replicates for each treatment group.
(B) Venn diagram showing overlap of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) across cortisol vs. vehicle, cortisol vs. relacorilant, and cortisol vs. cortisol + relacorilant comparisons. 946 genes represent DEGs that change in the same direction that are denoted by glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-modulated genes and labeled in yellow in the Venn diagram.
(C) Volcano plot showing differences in mRNA levels of all genes in the cortisol vs. vehicle condition. GR-modulated genes are labeled in yellow. Gene names are shown for the top 5 most significant and most fold-changing downregulated and upregulated genes.
(D) Gene ontology (GO) biological process analysis of GR-modulated genes. GO analysis was performed using WebGestalt (WEB-based Gene SeT AnaLysis Toolkit) (Liao et al., 2019).
(E) Normalized count plots of representative GR-modulated genes FKBP5, ZBTB16, and OPCML in vehicle, cortisol, relacorilant, and cortisol + relacorilant samples.