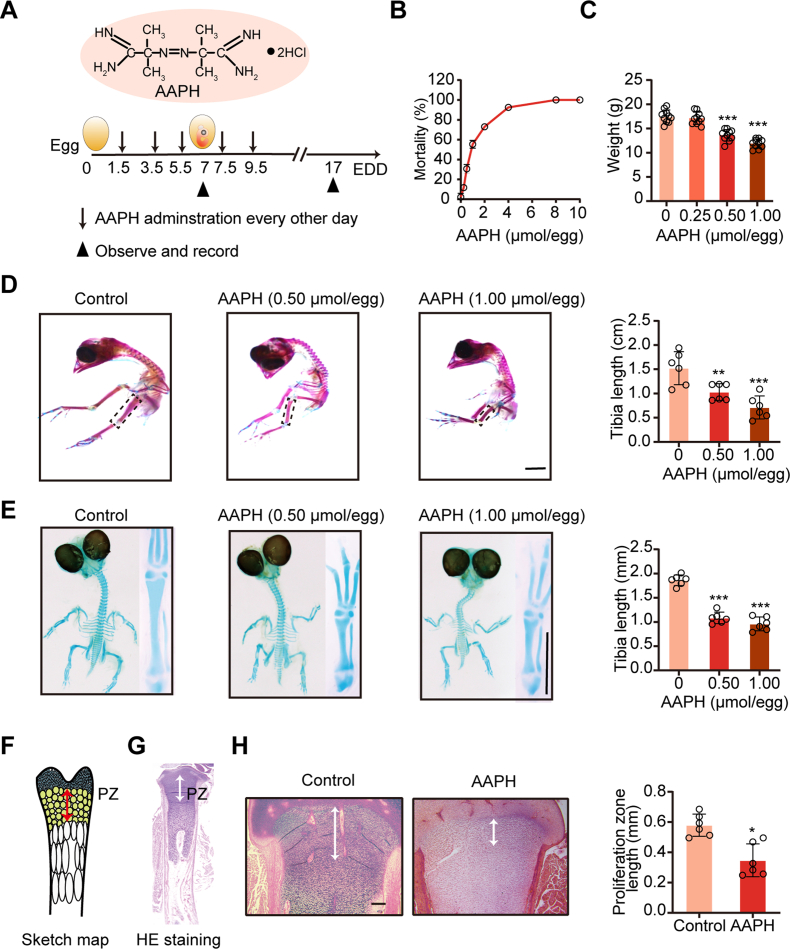
Fig. 1.
Alkoxyl radicals exposure restrict embryonic limb growth. (A) Schematic diagram establishing a chronic oxidative injury model in chicken embryos by injecting alkoxyl radicals generator AAPH into the albumen of eggs. The first day of incubation is considered as the initiation day of embryonic development and is termed as embryo development day (EDD). (B) The mortality and (C) body weight of chicken embryos were measured on EDD17. (D) Representative images of alcian blue and alizarin red-stained tibia and the quantification of tibia length of EDD17 embryos. Scale bar, 1 cm. (E) Representative images of the alcian blue-stained tibia and the quantification of tibia length of EDD7 embryos. The whole embryos and tibias were photographed. Scale bar, 1 mm. (F) The schematic diagram of the growth plate subregions. PZ indicates proliferative zone. (G) H&E staining of tibial growth plate. (H) H&E staining of the tibial PZ mapping the white double-head arrows on EDD17. Scale bar, 200 μm. Quantification of tibial proliferation zone is shown in the right panel. AAPH, 0.50 μmol/egg. Data are represented as mean ± SD. Comparisons between groups were made using one-way ANOVA (C–E) and Student's t-test (H). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs the Control group. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)