Fig. 1.
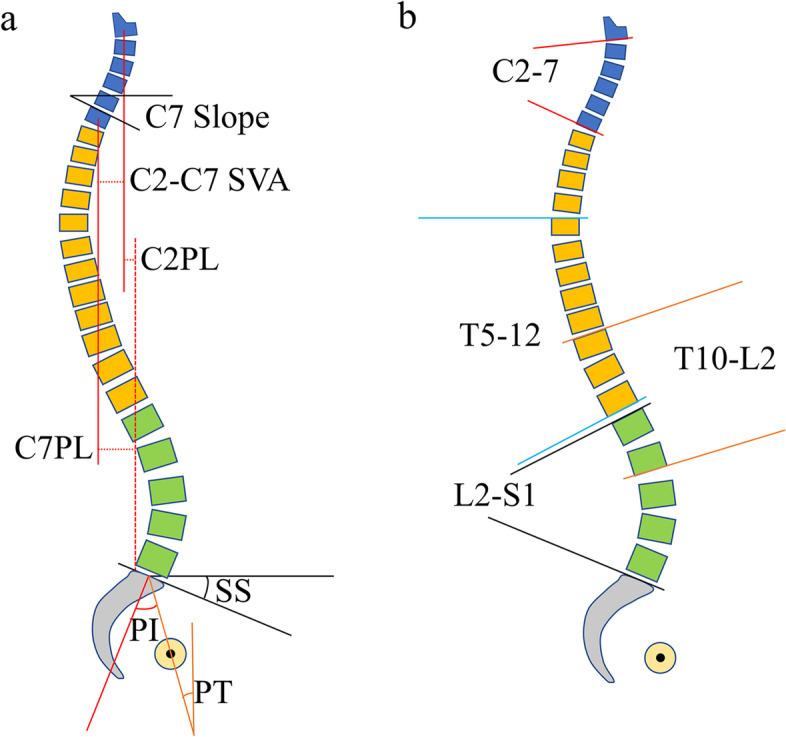
a C7 Slope, C2-7 plumb line (PL), C2-S1 Sagittal Vertical Axis (SVA), C7-S1 SVA, pelvic incidence (PI), pelvic tilt (PT), sacral slope (SS). b C2-C7 Cobb, T5-12 Cobb, T10-L2 Cobb, L1-S1 Cobb. a C7 slope was formed by the horizontal plane and the upper end plate of C7. C2 plumb line and C7 plumb line were defined as the vertical line (PL) drawn from the middle of the body of C2 or C7 vertebral body. C2-S1 SVA and C7-S1 SVA were defined as the horizontal distances from the C2 PL or C7 PL to the posterior superior corner of the sacrum (S1). The deviation of C2 PL and C7 PL was defined as C2-7PL. The PI corresponded to the angle between the perpendicular to the upper S1 level passing through its center and the line connecting this point to the axis of the femoral heads. The PT was defined by the angle between the vertical and the line connecting the center of the sacral endplate to the axis of the femoral heads. The SS was defined by the angle between a line tangent to the upper S1 endplate and horizontal line. b C2-7 Cobb angle was measured from the inferior endplate of C2 to the inferior endplate of C7. T5-T12 Cobb angle was measured from the superior endplate of T5 to the inferior endplate of T12 (Fig. 1b). T10-L2 Cobb angle was measured from the superior endplate of T10 to the inferior endplate of L2. L1-S1 Cobb angle was measured from the superior endplate of L1 to the superior endplate of S1
