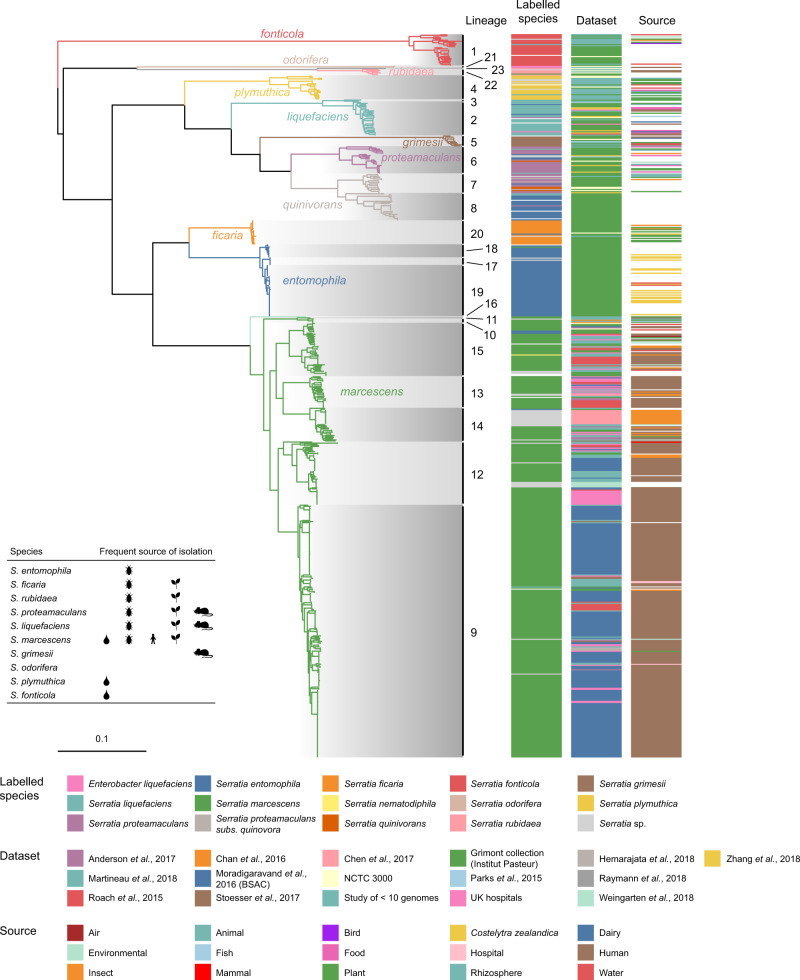
Fig. 1. Phylogeny of the genus Serratia.
Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree constructed from polymorphic sites of a core-gene alignment comprised of 2252 genes from 664 Serratia genomes, comprising 408 genomes from publicly available databases and 256 sequenced in this study. Tree constructed with 1000 ultrafast bootstraps. The core-gene alignment was produced from a Panaroo pan-genome analysis run with ‘–clean_mode moderate’ and the protein family threshold set to 70% shared sequence identity. Branches are coloured according to phylogroups defined by clustering assemblies at 95% ANI. Clades are shaded according to lineage, calculated through hierarchical bayesian clustering to three levels using FastBaps. ‘Labelled species’ refers to the labelled name of species on the provided Serratia strain sample, or species name associated with published Serratia genome sequences in the NCBI GenBank database. The inset illustrates the frequent sources of isolation of each species21, with symbols representing water, insects, human, plants and small mammals. The phylogenetic tree is reproduced in Supplementary Fig. 1 with the addition of the outgroup root, the country of isolation for each strain, and bootstrap values.