Fig. 7.
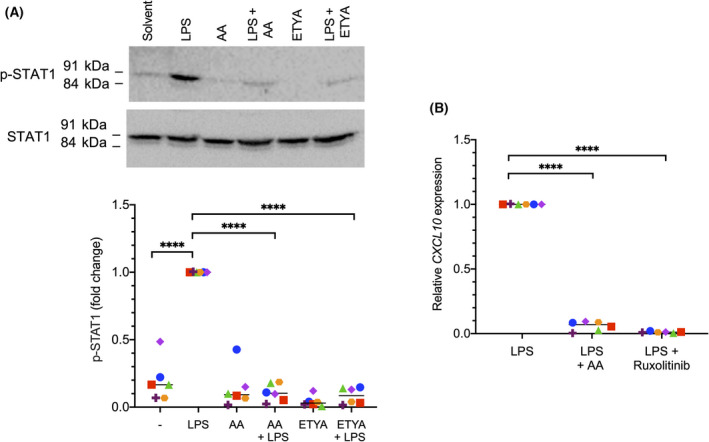
Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)‐induced STAT1 signaling in monocyte‐derived macrophages (MDMs) by arachidonic acid (AA). (A) Inhibition of LPS‐induced phosphorylation of STAT1 (Y701) by AA or 5,8,11,14‐eicosatetraynoic acid (ETYA). MDMs were pretreated with 50 µm of AA or ETYA for 30 min prior to stimulation with 100 ng·mL−1 LPS for 60 min. A representative immunoblot and quantification of six replicates are displayed. (B) RT‐qPCR analysis showing inhibition of CXCL10 by AA and verification of CXCL10 as a STAT1 target gene (n = 6 donor; represented by different symbols). MDMs were pretreated with 50 µm AA or the 0.5 µm of the STAT1 inhibitor Ruxolitinib for 30 min prior to stimulation with 100 ng·mL−1 LPS for 3 h. Statistical significance was analyzed by paired t test (****P < 0.0001). Horizontal lines indicate the median.
