Fig. 1.
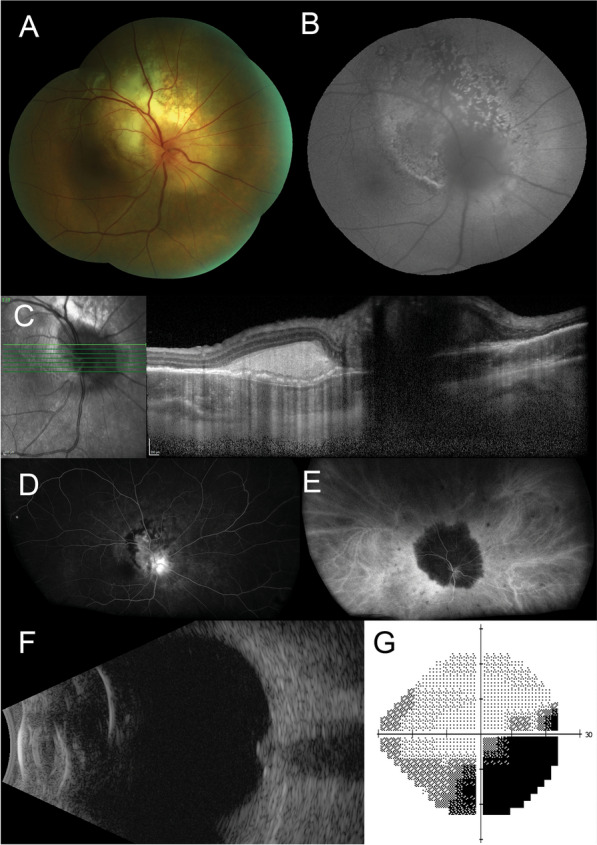
A Color fundus photograph of the right eye reveals a large, white, subretinal lesion centred on the optic nerve head. B Fundus autofluorescence shows a speckled picture. C Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography scan of the right macula shows a hyperreflective subretinal mass. D Fluorescein angiography demonstrates diffuse hyperfluorescence, focused over the peripapillary, subretinal lesion and blocked fluorescence at its margin with no significant leakage. E Indocyanine green angiography shows absolute blockage of fluorescence by the lesion with multiple smaller hypofluorescent spots in the peripheral retina. F An axial 12 o’clock meridional B-scan ultrasound demonstrates an enlargement of the optic nerve head with no retrobulbar extension. G Grayscale map from the Humphrey visual field test using a 24–2 pattern, shows a right inferotemporal scotoma
