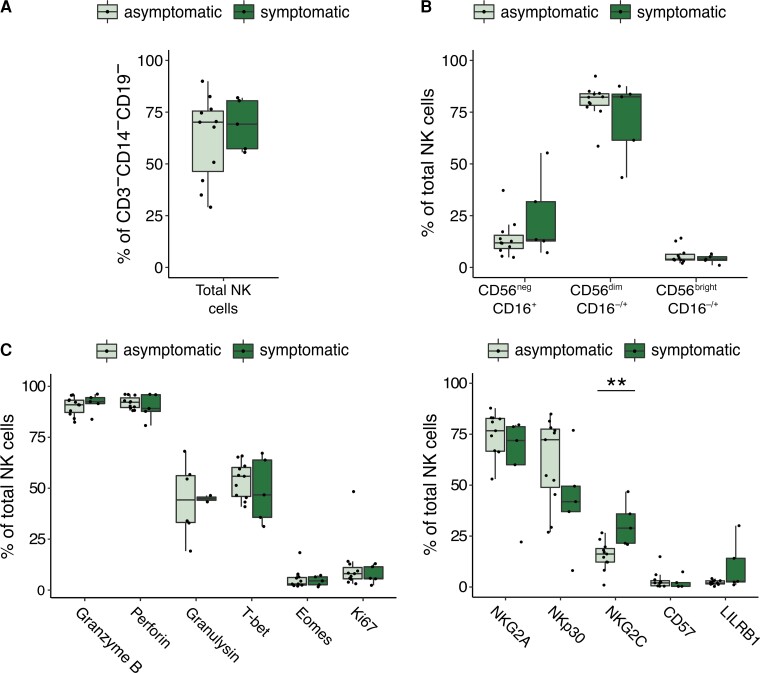
Figure 4.
NK-cell phenotype in symptomatic and asymptomatic cCMV cases. A, Frequency of total NK cells defined as CD3−/CD14−/CD19−/CD7+ lymphocytes in cord blood from symptomatic (n = 5, dark green) and asymptomatic (n = 11) cCMV-positive newborns. Newborns are defined as symptomatic if they demonstrated severe microcephaly and/or were small for gestational age at birth. B, Frequency of NK-cell subsets out of total NK cells in cord blood derived from symptomatic (n = 5) and asymptomatic (n = 11, light green) cCMV-positive newborns. C, Frequency of NK cells expressing granzyme B, perforin, granulysin, T-bet, eomesodermin, and Ki67 in symptomatic (n = 5) and asymptomatic (n = 11) cCMV-positive newborns. D, Frequency of NK cells expressing NKG2A, NKp30, NKG2C, CD57, and LILRB1 in symptomatic (n = 5) and asymptomatic (n = 11) cCMV-positive newborns. **P < .01. For gating strategy of NK-cell subsets refer to Figure 1A for (A, B, and D), and Supplementary Figure 2B for (C). Abbreviations: cCMV, congenital cytomegalovirus; NK cell, natural killer cell.