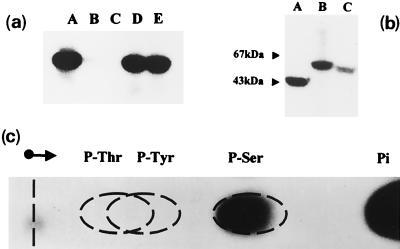
FIG. 2.
In vitro phosphorylation of purified hexosephosphate mutases. The pure enzymes were assayed for in vitro phosphorylation in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP, and reaction mixtures were analyzed by SDS-PAGE as described in the legend to Fig. 1. (a) Autophosphorylation of wild-type and mutant GlmM enzymes. Lane A, wild-type GlmM; lane B, mutant S100A; lane C, mutant S102A; lane D, mutant S327A; lane E, mutant S413A. (b) Autophosphorylation of other hexosephosphate mutases. Lane A, E. coli GlmM; lane B, rabbit muscle PGM; lane C, yeast N-acetylglucosamine-phosphate mutase Agm1p. (c) Identification of the labeled phosphoamino acid. A pure sample of wild-type GlmM enzyme was incubated with [γ-32P]ATP and acid hydrolyzed as described in Materials and Methods. Authentic standards of phosphothreonine (P-Thr), phosphotyrosine (P-Tyr), and phosphoserine (P-Ser) (200 nmol of each) were added to the protein hydrolysate, and the mixture was subjected to high-voltage paper electrophoresis. Phosphoamino acids were detected by staining with ninhydrin, and labeled compounds were detected by autoradiography. Pi, inorganic phosphate.