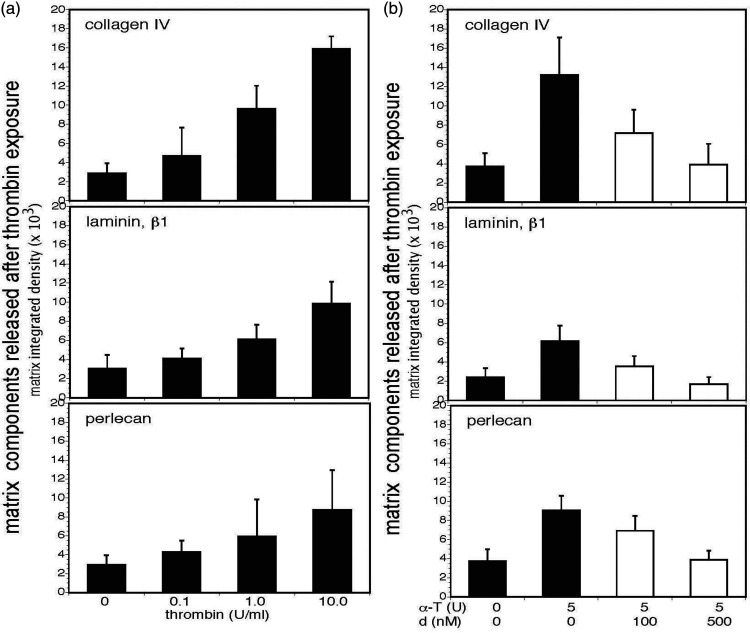
Figure 2.
α-thrombin releases matrix products from homogenates of cerebral cortex and dabigatran etexilate prevents their release. Panel a. Concentration-dependent release of products of collagen IV (α1-chain), laminin (β1-chain), and perlecan was detected by immunoblot when homogenates of freshly perfused cortical tissues from naïve adult mice were incubated with α-thrombin (0–10 U/ml) (black bars). Significant differences in the integrated density levels of each purified matrix protein, relative to α-thrombin concentration, were observed: collagen IV, p < 1 × 10−10; laminin, p < 1 × 10−8; and, perlecan, p = 0.002. With each matrix protein there was a significant trend toward increased degradation of the matrix proteins as the concentration of α-thrombin increased. For select individual comparisons, α-thrombin 0U/ml vs 1.0 U/ml: collagen IV, p < 0.0001; laminin, p < 0.0001; and, perlecan, p = 0.0157. Each bar represents n = 9 independent observations and Panel b. Dabigatran etexilate inhibited matrix collagen IV, laminin, and perlecan degradation in homogenates of murine cerebral cortex by 5U murine α-thrombin in a concentration-dependent manner (white bars). Integrated density levels of each matrix protein were significantly different: collagen IV, p < 1 × 10−7; laminin, p < 1 × 10−8; and, perlecan, p < 1 × 10−9. The multiple comparison pattern of perlecan was identical to that of laminin: all pairwise comparisons among the four thrombin combinations were significant, with the exception of the 0/0 vs 5/500 comparison (Bonferroni, α = 0.05). For select individual comparisons, at α-thrombin (α-T) 5 U/ml, dabigatran (d) 0 nM vs100 nM: collagen IV, p = 0.0019; laminin, p = 0.0004; and, perlecan, p = 0.0071. Each bar represents n = 9 independent observations.