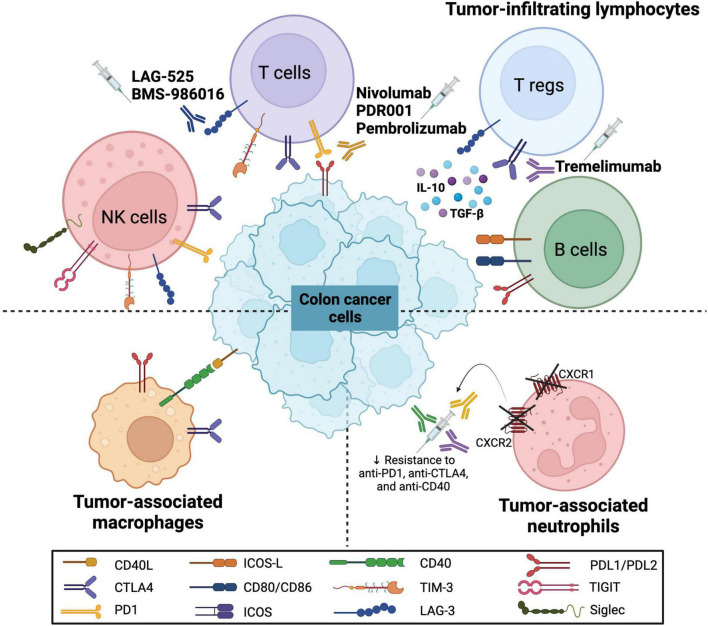
FIGURE 1.
Immune checkpoint molecules on various immune cells in colorectal cancer. The schematic representation shows the expression of various immune checkpoint molecules on immune cells that interact with colon cancer cells. These immune cells include tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) such as natural killer (NK) cells, T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs) and B cells, as well as tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs). The molecules include programmed cell death (PD1) and its ligand (PDL1/PDL2), CD40 and its ligand (CD40L), CD80/CD86, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 (CTLA4), T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 (TIM-3), lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG-3), identification of the inducible T cell co-stimulator (ICOS) and its ligand (ICOS-L), T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains (TIGIT) and sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectins (Siglec). Furthermore, several monoclonal antibodies have been introduced to target these molecules (LAG-3, PD/PD-L axis, and CTLA4) as potential CRC immunotherapeutic agents.