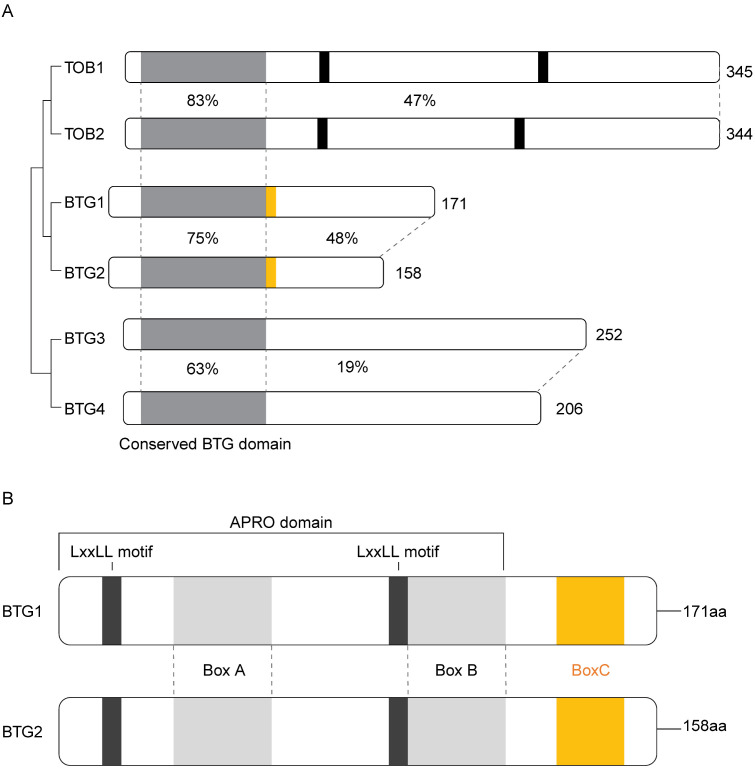
Fig. 1.
Summary of human BTG/Tob protein family. (A) The schematic dia-gram shows amino acid sequence-based similarities between the BTG/Tob family members. Indicated are the total length of the proteins and simi-larity rate (percentage) of amino acids in the BTG domain (light gray) and the C-terminal region. Also, the conserved PAM2 (black) and box c domain are shown in the schematic representations. (B) Domains of BTG1 and BTG2. The APRO domain, which is conserved in BTG1 and BTG2, contains three motifs; box A, box B, and box C. These boxes make it easier for proteins to interact with one another. Box C (yellow) is found only in BTG1 and BTG2. Box A is known to interact with CNOT7/8 and nuclear receptors. Box B is known for its association with CNOT7/8. Box C is required for interacting with PRMT1 and PABPC1. The core regions of BTG1 and BTG2 in-clude two LxxLL motifs (black), which are known to enhance nuclear receptor interaction.