Figure 10.
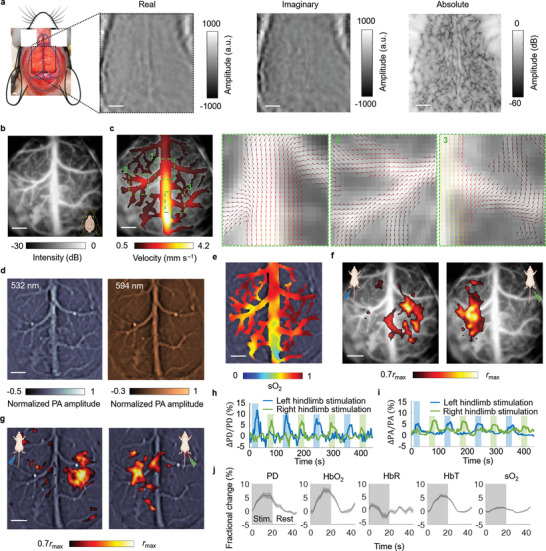
CRUST‐PAT of the mouse brain with the scalp and skull removed. a) Widefield CRUST images displayed with real, imaginary, and absolute pixel values. b) PDI of the mouse brain. c) Velocity amplitude map of the CBF in the cortical vessels. Regions 1–3 are magnified, showing detailed flow vectors at the blood vessel bifurcations. d) PAT images of the mouse brain acquired at 532‐ and 594‐nm optical wavelengths. The images are normalized to the maximum pixel values. e) sO2 map estimated using the PAT images acquired at the two wavelengths. f) CRUST‐measured functional responses presented using the Pearson correlation coefficients thresholded at 70% of the maximum, showing contralateral functional responses to the hindlimb electrical stimulation. g) PAT‐measured functional maps presented in the same way as (f). h) Temporal functional signal of CRUST, showing contralateral functional responses. The signal represents the moving average (4‐s temporal window size) of the mean values of the activated pixels in (f). i) PAT's temporal functional signal presented in the same way as (h), showing contralateral responses to the hindlimb electrical stimulation. j) Computed fractional changes of PD, hemoglobin concentrations, and sO2 signal in response to stimulation. Data are mean ± s.e.m., n = 8 stimulation cycles, technical replicates. For scale bars = 1 mm.
