Figure 2.
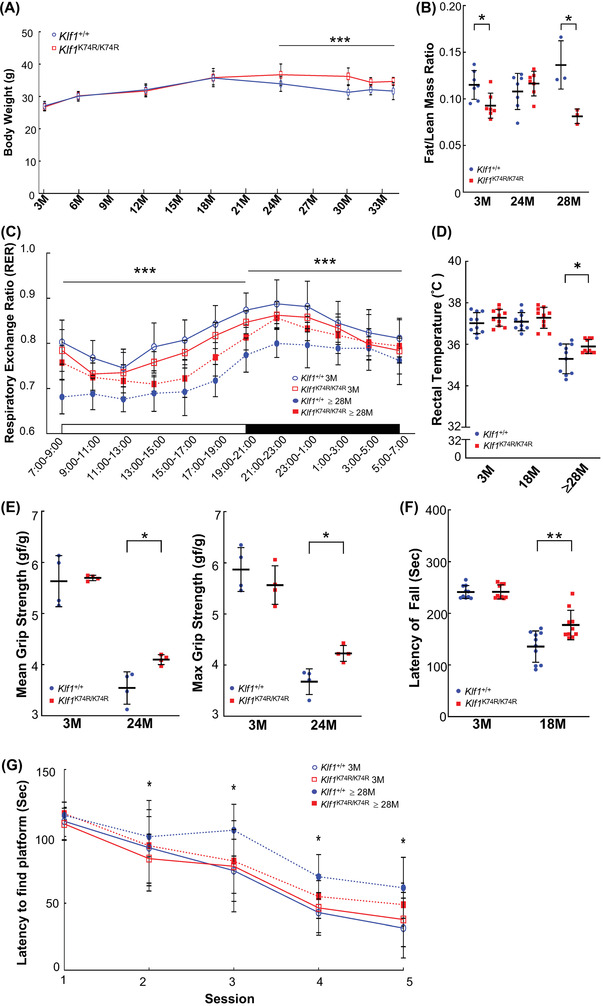
Genetically engineered Klf1 K74R/K74R mice exhibit increased healthspan. A) Body weights were recorded at ages 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 32, and ≥ 34 months; the number of mice in each group was 30, 30, 30, 30, 30, 30, 8, and 6, respectively. B) Fat/lean mass ratio of Klf1 K74R/K74R mice were compared with Klf1 +/+ mice at age 3, 24, and 28 months. The numbers of mice in each group were 7, 7, and 4, respectively. C) RER examination; the canonical diurnal metabolic parameters were measured in young (3 months old) and old (≥ 28 months old) Klf1 K74R/K74R and Klf1 +/+ mice (n = 6/group). D) Rectal temperatures were recorded at ages of 3, 18, and above 28 months (n = 10/group). E) Grip strength of Klf1 K74R/K74R and Klf1 +/+ mice was recorded at age 3 and 24 months (n = 4/group). F) Rotarod performance test. The latencies to fall from an accelerating rotarod were compared between Klf1 K74R/K74R and Klf1 +/+ mice at age 3 and 18 months, respectively (n = 10/group). G) Morris water maze test. The latencies of finding the platform underwater in different sections of training were compared between groups. All the data were assessed by ANCOVA or Student's t‐test and presented as mean ± SD and *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001.
