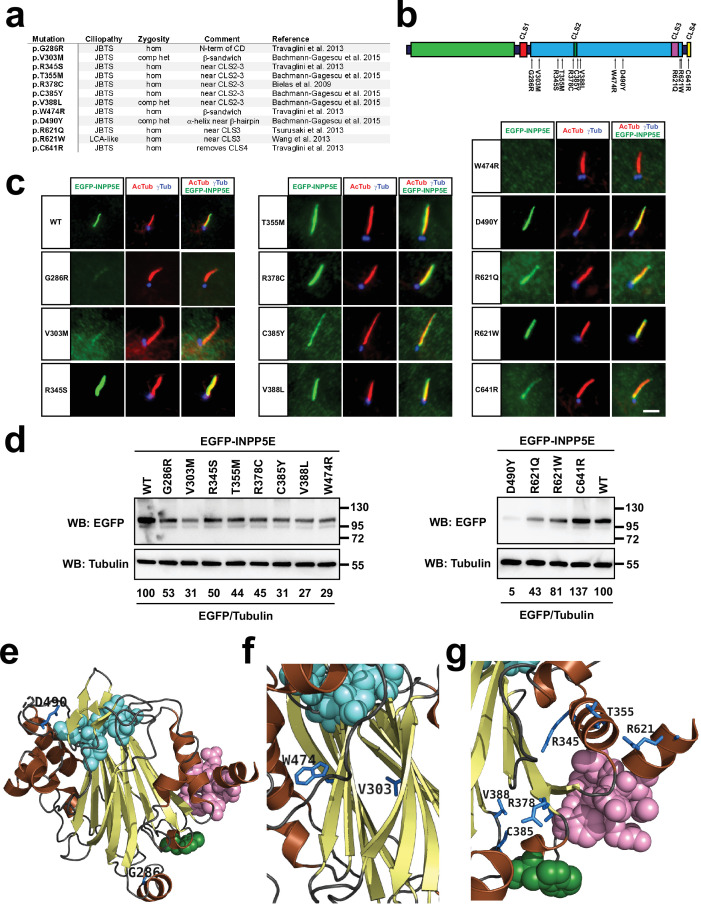
Figure 5. A subset of Joubert syndrome INPP5E mutations abolishes ciliary targeting.
(a) Table of INPP5E ciliopathy mutations analyzed here. JBTS: Joubert syndrome; LCA: Leber congenital amaurosis; hom: homozygous; comp het: compound heterozygous. (b) Schema of INPP5E protein sequence indicating the locations of the ciliopathy mutations from (c) relative to its four CLSs, its catalytic domain (cyan) and its N-terminal proline-rich region (green). (c) Ciliary localization of mutants from (a–b) was analyzed in hTERT-RPE1 cells as in Figures 1—3. Images are representative of at least two independent experiments per construct, with >30 transfected-cell cilia visualized per construct and experiment. Scale bar, 5 µm. (d) The mutants from (a–c) were expressed in HEK293T cells and their protein levels analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-EGFP antibody, and anti-alpha tubulin as loading control. Molecular weight markers in kilodaltons are shown on the right. The numbers under the tubulin blots are EGFP/Tubulin band intensity ratios, normalized so that WT equals 100%. (e–g) 3D views of INPP5E catalytic domain (PDB ID: 2xsw) showing the ciliopathy-mutated residues from (a) in dark blue (other colors as in Figure 4b). (e) Full catalytic domain showing G286 (bottom) and D490 (top left). (f) closeup view of beta-sandwich showing W474 and V303. (g) closeup view of CLS2-3 region showing R345, T355, R378, C385, V388L, and R621.