Figure 3.
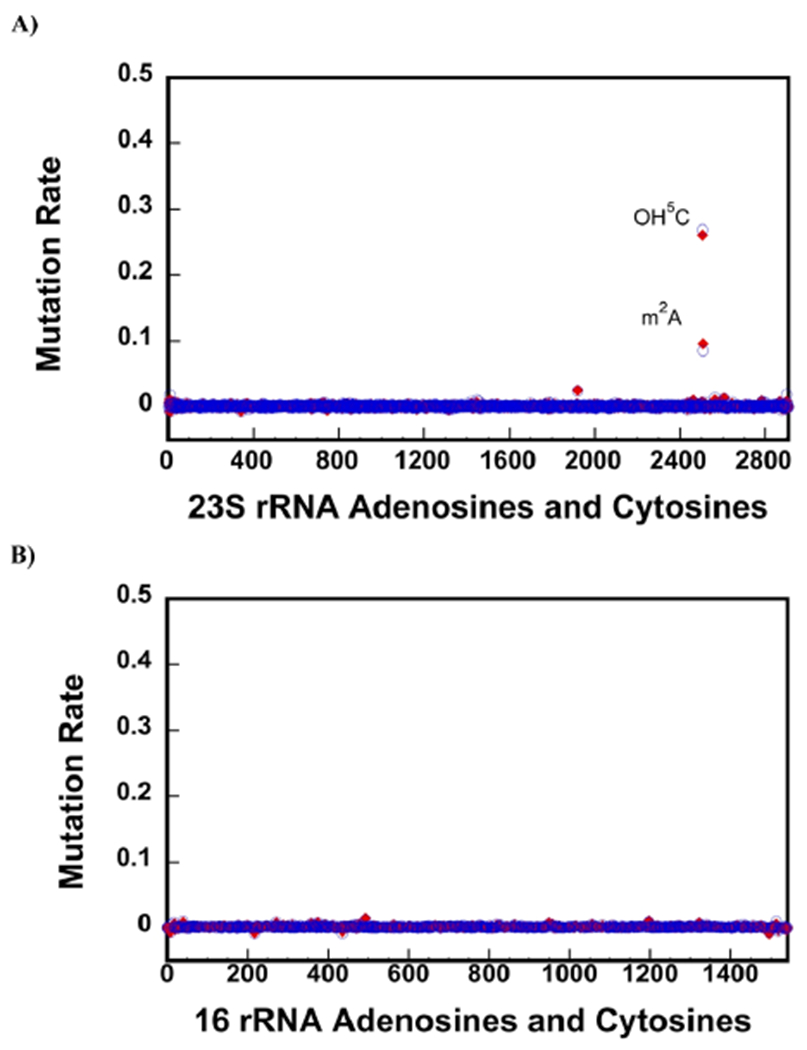
CMCT treatment followed by NaHCO3 exposure accurately detects OH5C and m2A modifications. (A,B) Background corrected mutation rates were calculated, as explained in the Materials and Methods section of the paper. Only the A and C residues are shown in the x-axes. The blue circles and the red diamonds are the data collected on two different biological samples. 23S rRNA of the native 50S large subunit contains one OH5C (2505) and m2A (2507). The background corrected mutation rates of OH5C 2505 and one m2A 2507 residues are significantly higher than the other C and A residues in 23S rRNA (A). Thus, employing CMCT and NaHCO3 treatment, we are able to detect both OH5C and m2A modifications and do not observe false positive OH5C or m2A modifications. There are no OH5C and m2A modifications in 16S rRNA of the 30S, and we do not observe false positive OH5C and m2A modifications in this RNA molecule (B).
