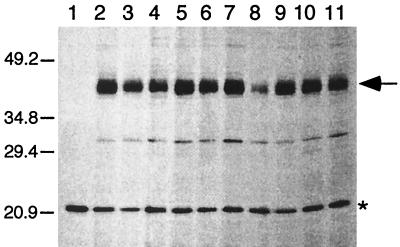
FIG. 2.
Fluorograph of radioactively labeled TetA(K) proteins prepared from E. coli BL21(DE3)/pLysS cell extracts containing plasmids encoding mutations at G159 in TetA(K). Lanes [extracts from cells harboring the following plasmids, with the normalized value for detected TetA(K) protein denoted as a percentage of the wild-type value]: 1, pBluescript II SK; 2, pSK4646 (wild type; 100%); 3, pSK4568 (G159A; 101.0%); 4, pSK4570, (G159R; 63.6%); 5, pSK4571 (G159D; 102.6%); 6, pSK4572 (G159N; 96.1%); 7, pSK4573 (G159E; 97.9%); 8, pSK4574 (G159P; 24.7%); 9, pSK4575 (G159S; 87.7%); 10, pSK4576 (G159T; 78.5%); and 11, pSK4577 (G159V; 64.8%). The positions of migration and sizes (in kilodaltons) of coelectrophoresed standard proteins are shown on the left. Products corresponding to the TetA(K) protein (43 kDa) are indicated on the right by the arrow, and a host-encoded protein, used for normalization of TetA(K) expression levels, is indicated by the asterisk. Only the relevant portion of the fluorograph is shown. Similar studies were performed for all TetA(K) mutant proteins; only one representative data set is presented here.