Figure 1: NSCLC cells with activating KRAS mutation are more responsive to CERK inhibition for effects on cell survival.
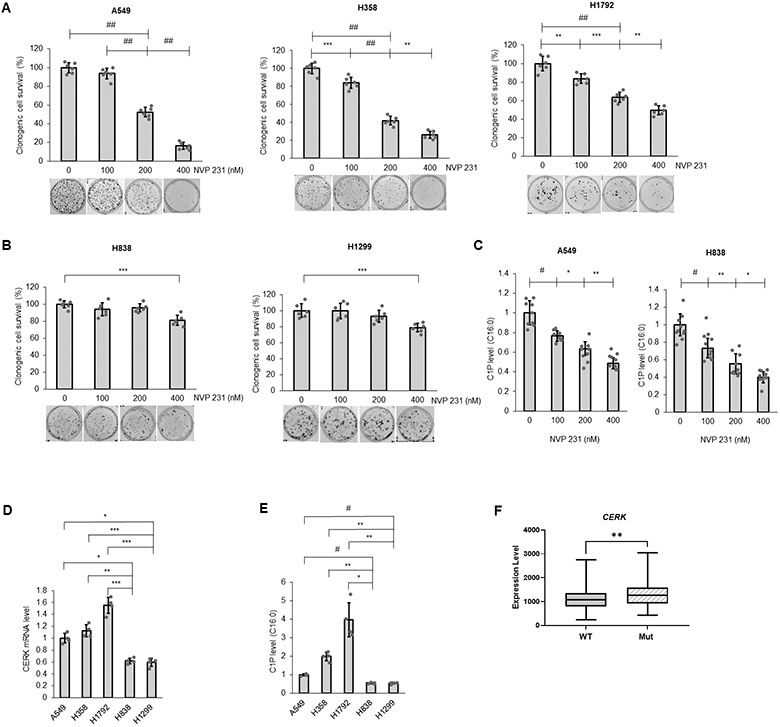
(A, B) NSCLC cells with Mut (A) or WT KRAS (B) were treated with NVP231 (0-400 nM) for 48 hours then utilized in clonogenic survival assay. (C) A549 (LUAD) and H838 (LUAD) cells were treated with NVP 231 as in (A) for 24 hours then subjected to mass spectrometry analysis for C16:0 C1P level (C16:0 C1P species represents the majority of total C1P detected in the NSCLC cell lines). (D, E) A549(LUAD)/H358(BAC)/H838(LUAD)/H1299(LCC) cells at approximately 40-50% confluency were placed in serum-free media for 16 hours, then cell lysates were subjected to RNA extraction followed by RT-qPCR assay for CERK mRNA quantification (D) or mass spectrometry analysis for C16:0 C1P level (E). (F) Comparison of CERK expression in human lung adenocarcinoma patients harboring WT versus Mut KRAS (G12 Mut); n = 305 for WT and 87 for Mut KRAS. Data in (A-E) are means ± SD; n = 6 from at least two independent occasions. *p<0.05, **p<0.005, ***p<0.0005, #p<0.00005, ##p<0.000005. Unless otherwise noted by an * or depicted p-value, data are not significant between depicted groups; p>0.05.
