Figure 3. Forest plots and meta-analysis of the covariate-adjusted regression analyses.
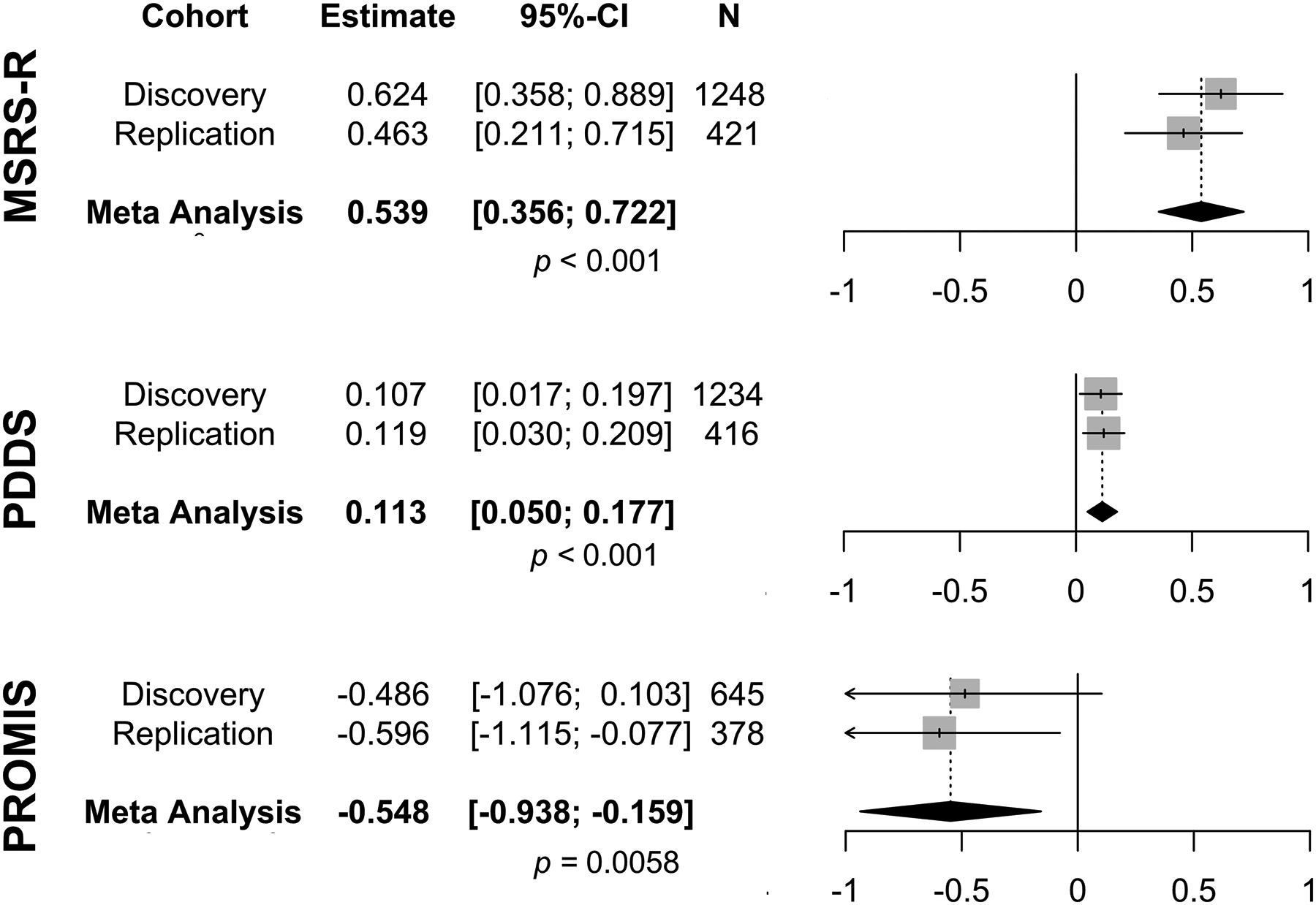
Area deprivation index in 2015 was the exposure for the median scores of the patient-reported outcomes of neurological and physical function from the latest year between 2018 and 2020. Higher scores of MS symptom burden (MSRS-R), higher scores of gait impairment (PDDS) and lower T-scores of PROMIS-physical function indicated greater neurological and/or physical disability. Each square was the standardized β coefficient, and each line was the 95% confidence interval (95%-CI). The diamond represented the meta-analyzed β coefficient and 95% CI in a random-effects meta-analysis of the two cohorts. Higher ADI was associated with subsequently greater MSRS-R and PDDS. The significance threshold for multiple testing was p=0.0167.
