Figure 3. The novel Arrdc4-knockout mouse model.
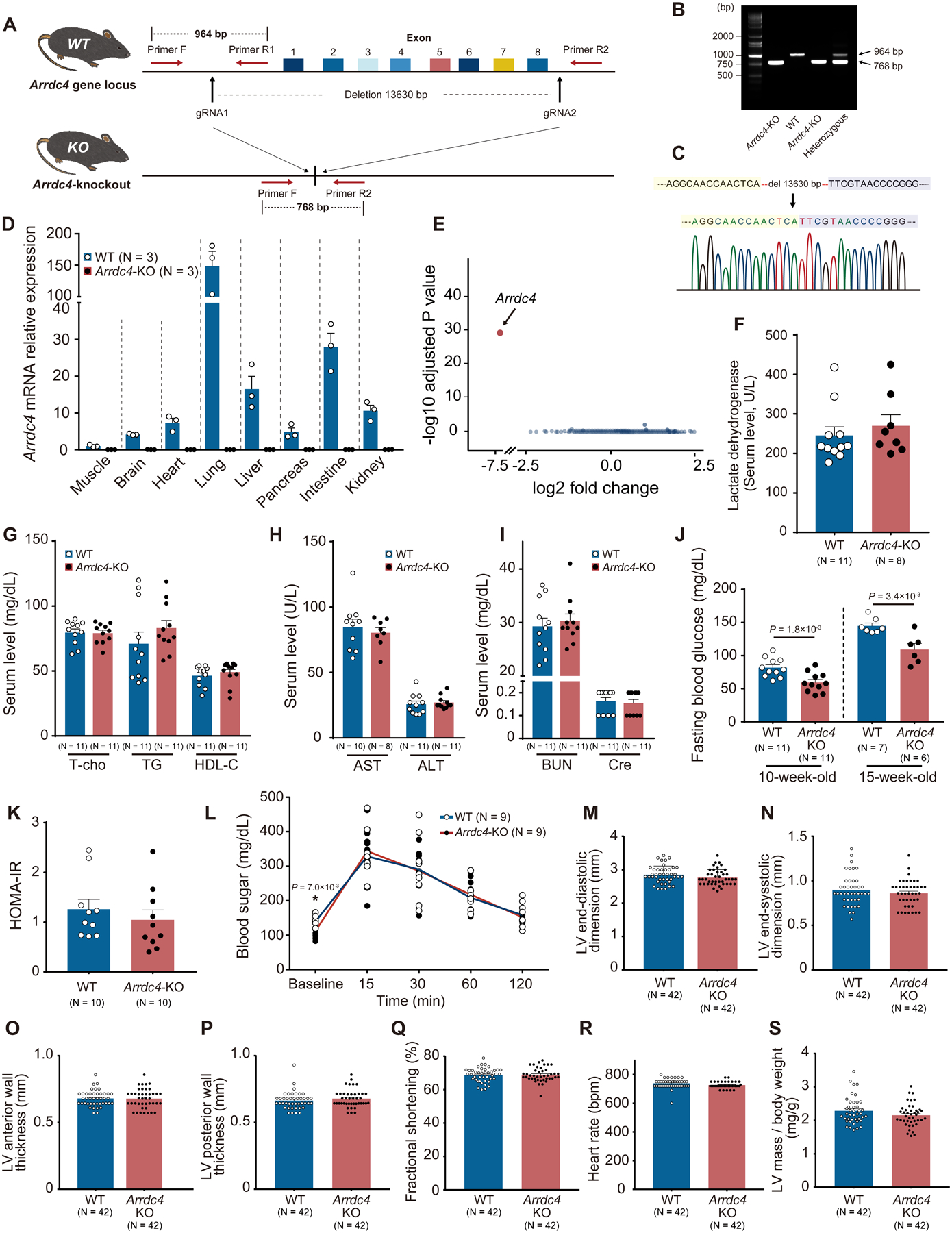
A. A pair of gRNA was designed to target the Arrdc4 locus. The gRNAs and Cas9 mRNA were microinjected into C57BL/6 embryos. B. Homozygous and heterozygous Arrdc4-knockout (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice were characterized by PCR with primers F, R1, and R2. C. Successful deletion of Arrdc4 exon1–8 was confirmed by DNA sequencing in the mouse. D. No significant Arrdc4 mRNA was expressed in multiple tissues from Arrdc4-KO mice quantified by quantitative PCR. E. Volcano plot of differentially expressed transcripts with spots representing up- or down-regulated genes in Arrdc4-KO hearts with fold change on X-axis and P-value on Y-axis. F-J. Detailed clinical chemistry was analyzed. After a fasting period of 6 hr, blood was obtained for biochemical analysis in 13-week-old mice (F-I, Mann-Whitney U test; J, t-test). K. Homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) was calculated from blood sugar and responsive serum insulin levels. P=N.S. (Mann-Whitney U test). L. Glucose tolerance test was performed by an intraperitoneal injection of 2 g glucose/kg body mass in mice (two-way ANOVA with repeated measures followed by Bonferroni test or *t-test for baseline comparison). M-S. Echocardiographic left ventricular (LV) parameters were measured in WT and Arrdc4-KO mice at baseline. P=N.S. between the genotypes (Mann-Whitney U test).
