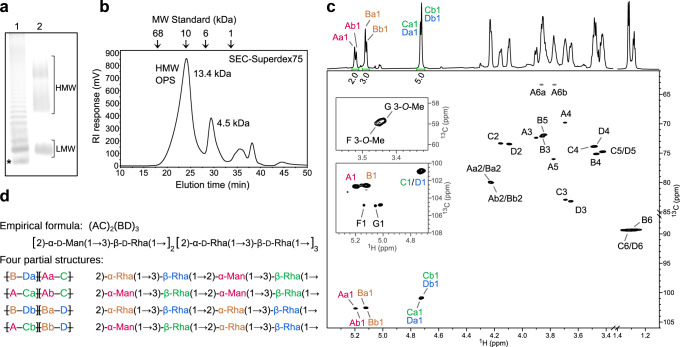
Fig. 1. Structure of the A. aeolicus O antigen.
a Representative SDS-PAGE of A. aeolicus VF5 LPS. Lane 1: Salmonella enterica LPS; Lane 2: A. aeolicus VF5 LPS. In lane 1, the LPS band with the smallest molecular weight is the lipid A-core (*). The subsequent bands above the lipid A-core is lipid A-core with one repeat unit consecutively added after each band. An uncropped gel image is shown as Source Data. b Size exclusion of purified O antigen. The polysaccharide elutes at the first peak with an average molecular weight of 13.4 kDa. c Partial 1H and 1H,13C-HSQC spectra of the released HMW O polysaccharide chain with signal assignments. Anomeric peak areas are shown below the 1H spectrum. The two insets of HSQC spectrum at lower contour levels show the anomeric and methyl group signals of the terminal residues F and G. The signals of rhamnose methyl groups (B6, C6 and D6) are aliased along F1 and their actual 13C chemical shifts are lower by 70 ppm. d Structural motifs present in A. aeolicus LPS O antigen. The partial structures illustrate the origin of the a/b non-equivalency in the major residues A, B, C and D. No regular repeating unit could be determined, so a semi-regular repeating structure is proposed.