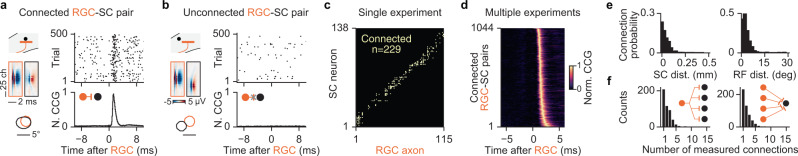
Fig. 3. Measuring afferent monosynaptic connections in vivo at a large scale.
a Examples of a monosynaptically connected RGC-SC pair. Raster plot of SC spiking activity triggered on RGC spike times (top). Cross-correlogram (CCG) between the RGC and SC spiking activity (bottom). The short latency peak in the CCG is a hallmark of synaptic connections in vertebrates. Note the close distance of the RGC axonal and SC neuronal waveforms on the probe (middle) and the overlapping RFs (bottom). b Unconnected RGC-SC pair. Unconnected pairs do not overlap in SC and visual space. c Connectivity matrix between RGC axons and SC neurons recorded in a single experiment. Yellow marks indicate connected pairs. RGC axons and SC neurons are sorted by their location in SC. d CCGs of connected pairs across multiple experiments, sorted by peak latency. e Connection probability as a function of SC distance and RF distance. f Number of measured RGC-SC connections per RGC axon (left) and SC neuron (right). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.