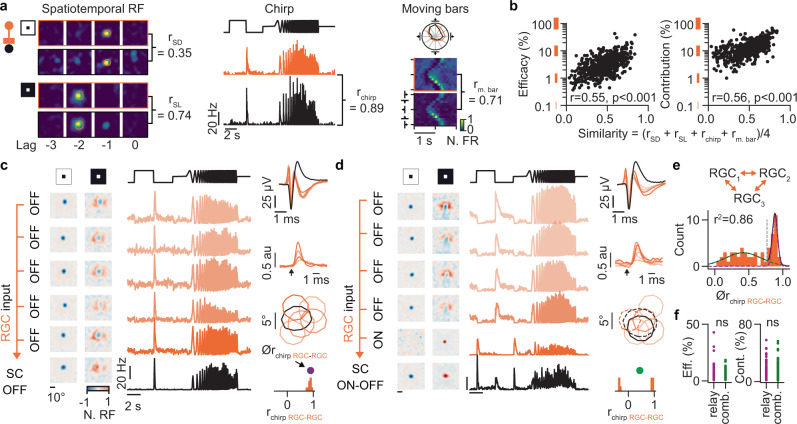
Fig. 5. Functional organization of the retinocollicular connections.
a Visually evoked activity in response to sparse noise (left), chirp (middle), and moving bars (right) of a connected RGC-SC pair. The functional similarity of the RGC axon (orange) and the postsynaptic SC neuron (black) is evident and characterized by the correlation coefficients rSD, rSL, rchirp and rm. bar. b The connection efficacy and contribution are correlated with the overall functional similarity between the RGC-SC pair. The overall functional similarity is estimated by the average of rSD, rSL, rchirp, and rm. bar. p = 1.36 × 10−43 and p = 5.59 × 10−45, Pearson correlation coefficient test, n = 526 connected pairs. c Relay motif example of an SC neuron receiving convergent inputs from a pool of RGCs with similar functional responses. Receptive fields (left). Responses to the chirp stimulus (middle). Spike waveforms, CCGs, contours of RFs, and the histogram of rchirp between RGC-RGC (orange) (right). The arrow in the CCG marks the RGC spike time. The magenta dot shows the average rchirp of the presynaptic RGC pool. d Combination motif example, same format as (c). Both ON and OFF RGCs converge onto the SC neuron. OFF-RFs shown as solid lines and ON-RFs as dashed lines. e Functional diversity of RGC convergent inputs to SC neurons. Histogram of the average rchirp between RGCs converging onto the same SC neuron. Note that some RGC input pools are very similar with rchirp values close to 1 while others convey a mixed input with lower rchirp values. Note that the distribution is bimodal with functionally similar pools (relay, magenta) and functionally diverse pools (combination, green) exist across the population of SC neurons (n = 57 SC neurons). f Connection efficacy and contribution are similar in relay (n = 104 pairs, p = 0.73) and combination (n = 138 pairs, p = 0.33). Two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.