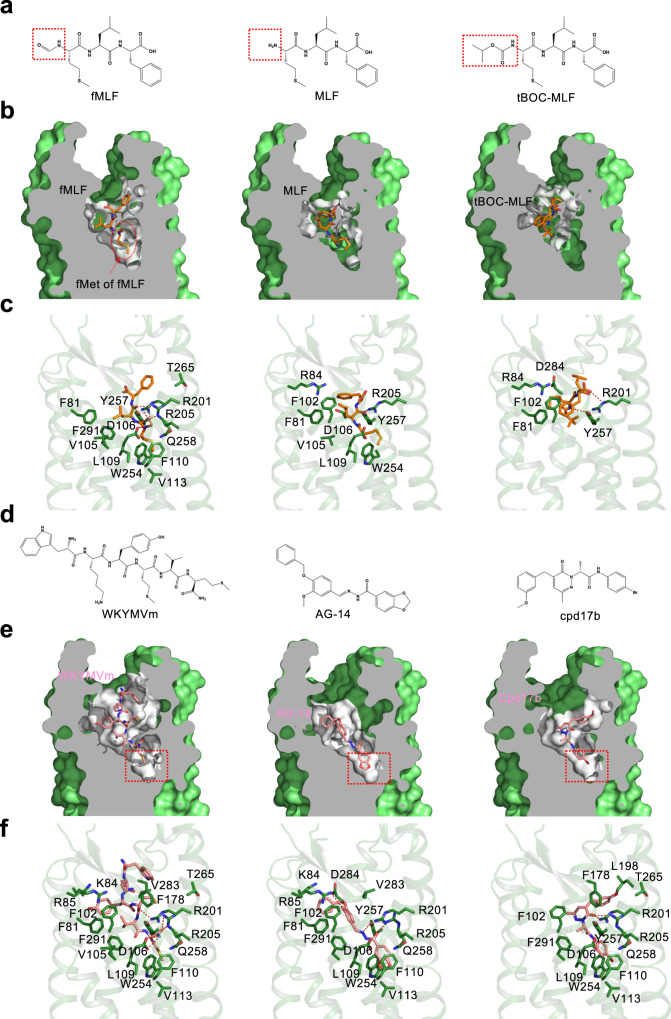
Fig. 4. Binding poses of fMLF, non-formyl analogs and small molecule ligands to FPR1.
a Chemical structure of fMLF and its non-formyl analogs. b Slab views of the binding pocket of fMLF (left, cryo-EM model), MLF (middle, docking model), and tBOC-MLF (right, docking model) in FPR1, respectively. The ligands are displayed in licorice with carbon in orange. The binding pocket is highlighted in white. c Molecular interaction of bound fMLF (left), MLF (middle), and tBOC-MLF (right) with the FPR1 binding pocket. d Chemical structures of WKYMVm, AG-14 and Compound 17b (Cpd 17b). e Slab views of the binding pocket of WKYMVm, AG-14 and Cpd 17b, all from docking models. f molecular interaction of bound WKYMVm (left), AG-14 (middle), and Cpd 17b (right) with the FPR1 binding pocket, respectively. The residues of FPR1 within 4.5 Å to the atoms of the ligands are shown as green licorice.