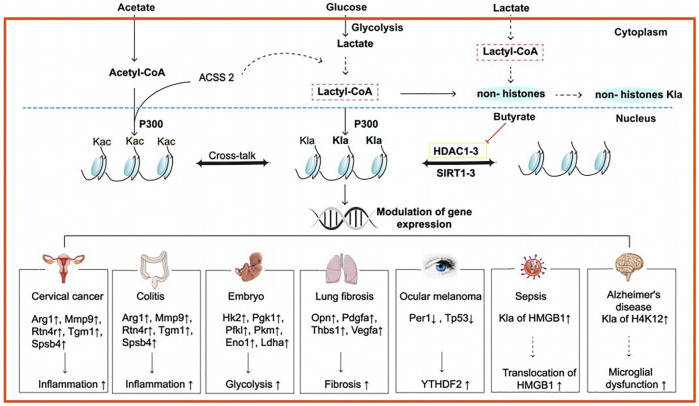
FIGURE 1.
Possible mechanism and roles of histone lactylation in some diseases. Lactate derives from the conversion of glucose by glycolysis, and it may synthesize lactyl-CoA, which is hitherto unclear with the ACSS2. Then, the lactyl group is transferred by p300 to Lys lactylations, leading to various physiopathological activities in different diseases. For example, in human cervical cancer and colitis, inflammation-related genes such as Arg1, Mmp9, Rtn4r, Tgm1, and Spsb4 are upregulated; in embryon, some glycolysis-related genes, including Hk2, Pgk1, Pfk1, Pkm, Eno1, and Ldha, are upregulated; in lung fibrosis, fibrosis-related genes such as Opn, Pdgfa, Thbs1, and Vegfa are upregulated; in ocular melanoma, two tumor suppressor genes, namely, Per1 and Tp53 are upregulated; In sepsis, Kla of HMGB1 is upregulated, contributing to the translocation of HMGB1; in AD, Kla of H4K12 is upregulated, resulting in microglial dysfunction. Abbreviations: ACSS2, synthetase short-chain family member 2; p300, an acetyltransferase; Arg1, arginase1; Mmp9, matrixmetalloproteinase9; Rtn4r, reticulon 4 receptor; Tgm1, transglutaminase 1; Spsb4, SPRY domain- and SOCS box-containing protein 3; Hk2, hexokinase 2; Pgk1, phosphoglycerate kinase1; Pfk1, phosphofructokinase-2; Pkm, pyruvate kinase M2; Eno1, enolase1; Ldha, lactate dehydrogenase; Opn, osteopontin; Pdgfa, platelet-derived growth factor A; Thbs 1, thrombospondin-1; Vegfa, vascular endothelial growth factor A; Per1, period circadian regulator 1; Tp53, tumor suppressor gene TP53; the dashed lines mean that the process has not been proved; The solid lines mean that the process has been proved.