Figure 3. Phosphorylation of PRKAR1A inhibits PKA activity.
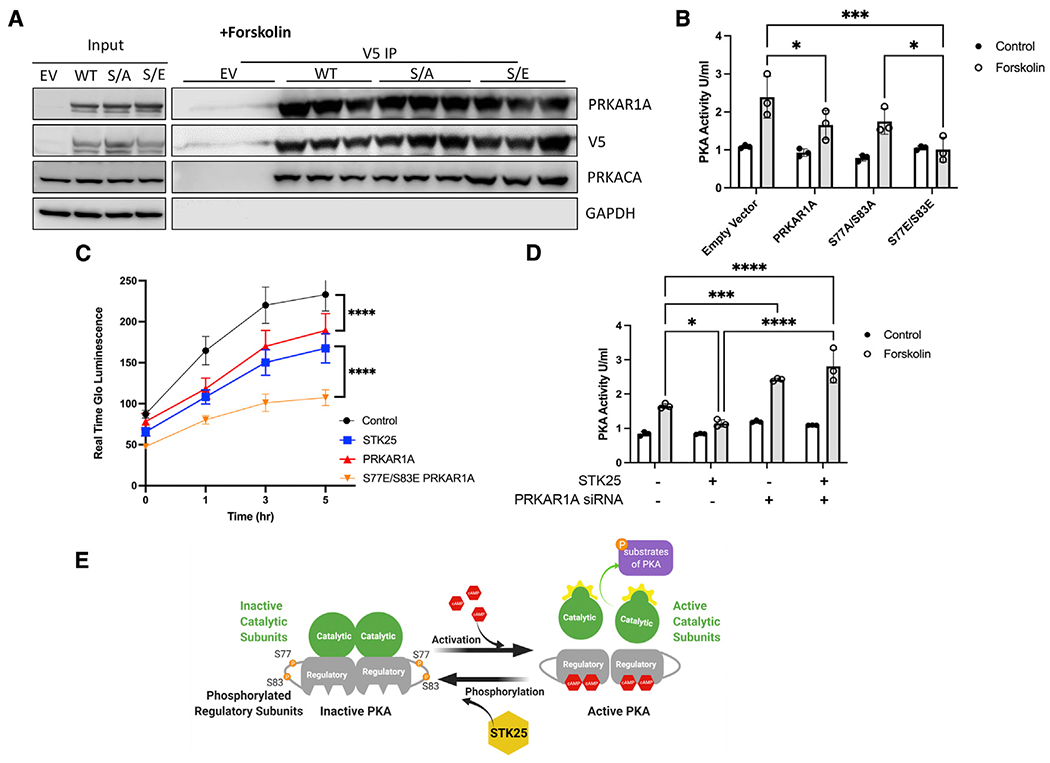
(A) Co-immunoprecipitations of V5-tagged PRKAR1A, S77A/S83A PRKAR1A, or S77E/S83 PRKAR1A and immunoblotting for PRKARCA in HEK293T cells stimulated with forskolin (10 μM, 30 min). n = 3 for each condition.
(B) PKA activity in HEK293T cells stimulated with forskolin (10 μM, 30 min) and transfected with EV, wild-type PRKAR1A, S77A/S83A PRKAR1A mutant, or S77E/S83E PRKAR1A mutant as indicated.
(C) HEK293T cells transfected with the indicated vectors and assessed for growth by Real Time Glo for 5 h after stimulation with forskolin (10 mM). A representative Real Time Glo assay analyzed in sextuplicate ±SEM is shown.
(D) PKA activity in HEK293T cells stimulated with forskolin (10 μM, 30 min) and either overexpressing STK25 and/or the siRNA of PRKAR1A.
(E) Model of STK25 downregulation of the PKA pathway through phosphorylation of PRKAR1A.
For all graphs in this figure, n = 3 for each condition, data are presented as mean ± SD and analyzed in technical triplicates, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 by ANOVA with Tukey’s adjustment for multiple comparisons.
See also Figure S2.
