Figure 3.
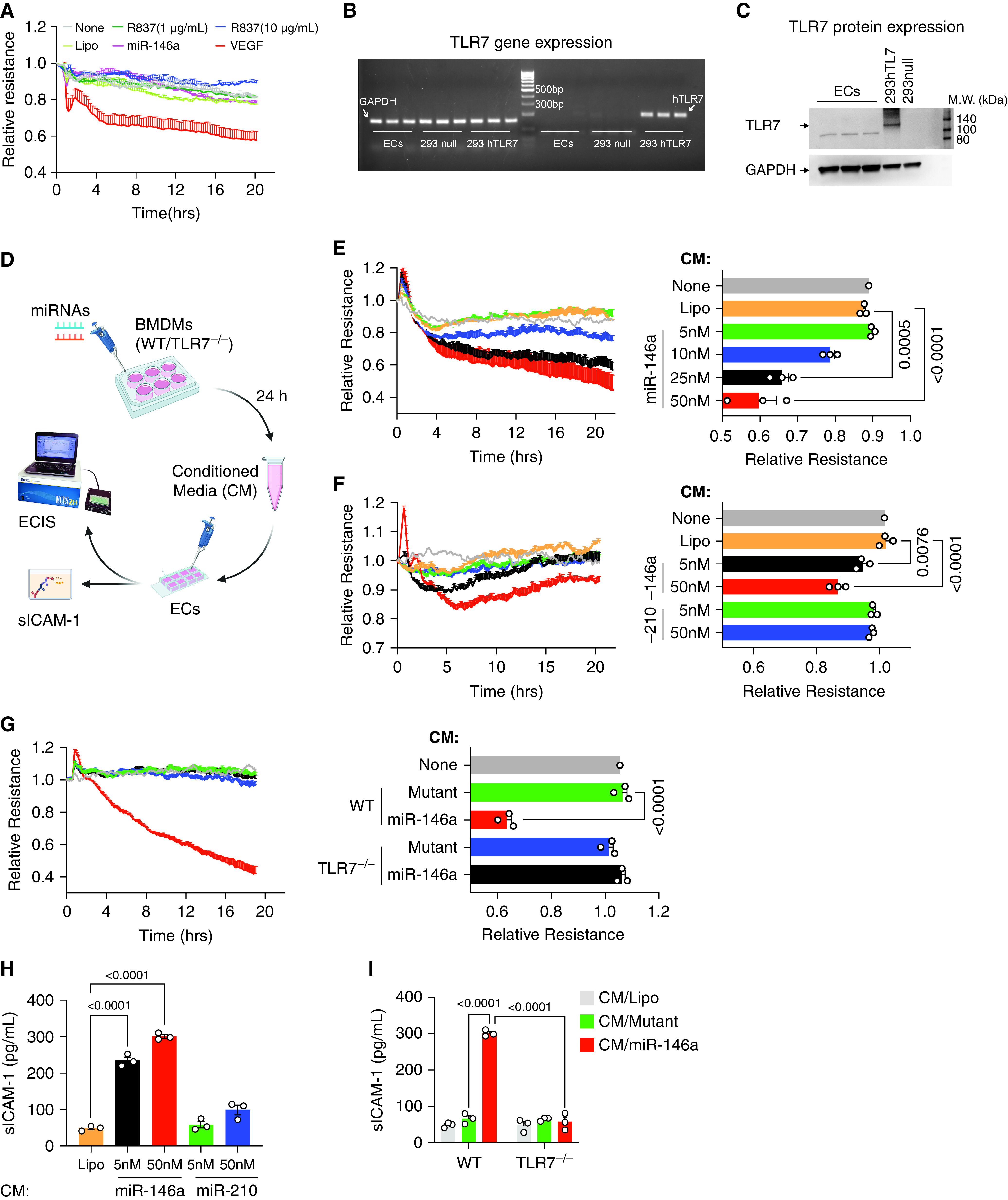
miR-146a-5p increases endothelial permeability via macrophage TLR7. (A) Neither miR-146a-5p (50 nM) nor TLR7 agonist R837 increased permeability in endothelial cells (ECs) tested by electric cell-substrate impedance system (ECIS). Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF, 200 ng/ml) was used as a positive control. The ECIS curves are from duplicate samples. The experiment was repeated once in triplicates with similar results. (B–C) No TLR7 gene and protein expression was detected in endothelial cells. HEK293 null cell (293 null) served as a negative control, and HKE293 overexpressing human TLR7 (293 hTLR7) served as a positive control. (D) Schematic experiment flowchart. ECs were treated with 20% conditioned media (CM) collected from macrophages (BMDMs) (WT and TLR7−/−) incubated with either Lipofectamine (Lipo), miR-146a-5p, or miR-210-3p at various dosages for 24 hours. Resistance was measured by ECIS, and sICAM-1 (secreted intercellular adhesion molecule 1) was tested using ELISA. (E–G) Conditioned media from miR-146a-5p (proinflammatory miRNA) but not that of miR-210 (nonproinflammatory miRNA) increased EC permeability via macrophage TLR7. Resistance at 10 hours was quantified for statistical analysis and presented as a bar graph. (H) sICAM-1 concentrations were measured by ELISA after designated CM treatment in (F) and (G). Data were presented as mean ± SEM. Data of (E) were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test. Data of (F), (G), and (H) were analyzed using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test. BMDM = bone marrow-derived macrophages; miRNA = microRNA.
