Figure 7.
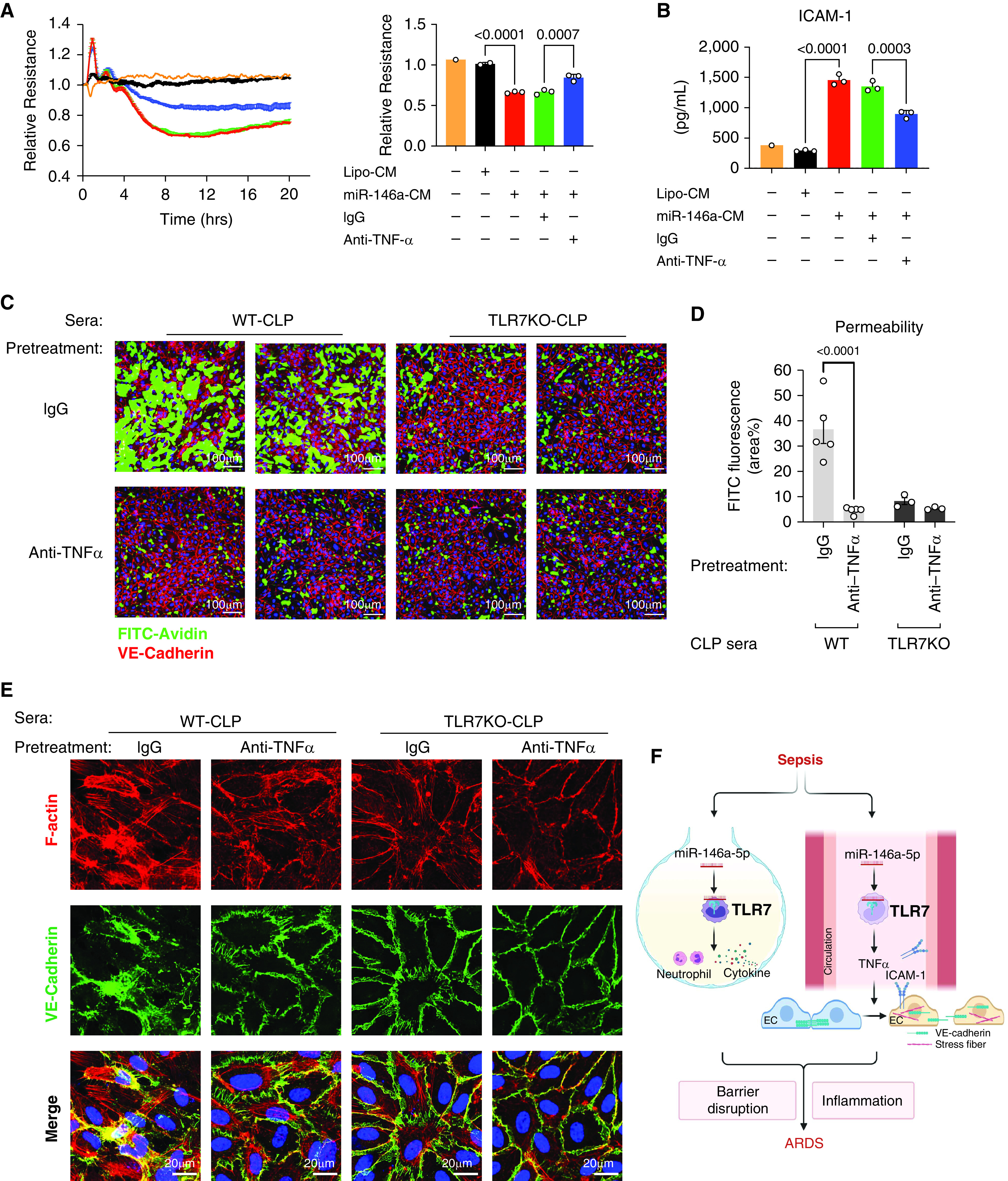
Block TNFα reduces permeability induced by conditioned media and septic sera in ECs. CM or septic sera were incubated with anti-TNFα antibody or control IgG for 45 minutes at room temperature before the treatment. (A) Resistance of ECs was measured and quantified at 10 hours as a bar graph after treatment of CM pretreated with anti-TNFα (1 μg/ml) or IgG (1 μg/ml). Experiments were performed in duplicates or triplicates and repeated at least twice. (B) Media ICAM-1. (C) Representative XperT images of ECs after treatment of sera pretreated with anti-TNFα (10 ng/ml) or IgG (10 ng/ml). (D) Endothelial permeability was quantified by the area percentage of FITC in XperT images. n = 5 per group. (E) VE-cadherin disruption and stress fiber formation in ECs. (F) Schematic illustration of how TLR7 mediates sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Cellular miR-146a-5p is released into the alveolar space and circulation after CLP-induced sepsis, which then binds to and activates TLR7 signaling. TLR7 stimulation in the alveolar space induces neutrophil accumulation and inflammatory cytokine production. On the other hand, TLR7 activation in the blood causes endothelial activation and hyperpermeability via its downstream effector TNFα by modulating the structure of VE-cadherin and the formation of stress fiber. Barrier disruption and inflammation then lead to ARDS. Graph was created with BioRender.com. Data were presented as mean ± SEM and analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test (A–B) or two-way ANOVA (D) with Bonferroni’s post hoc test.
