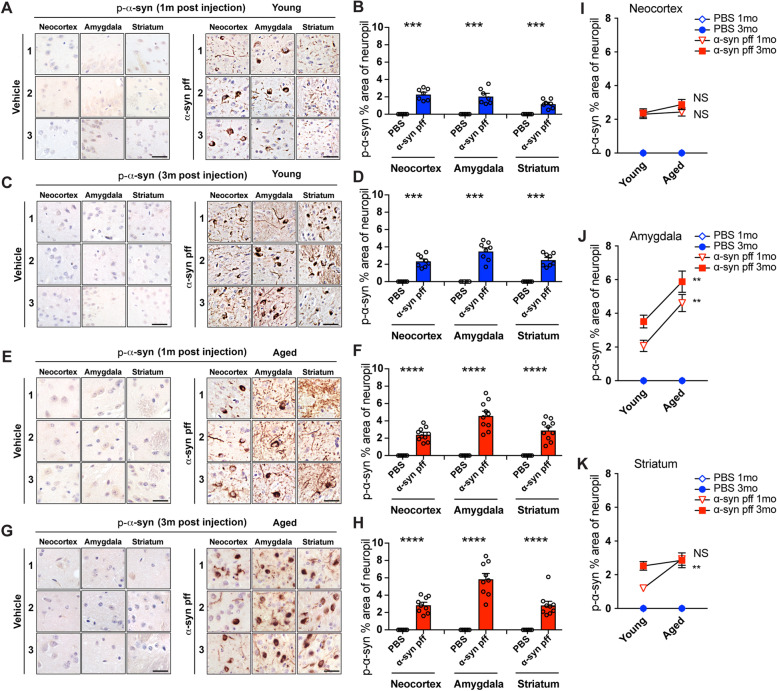
Fig. 1.
Phosphorylated-ɑ-syn immunostaining in young and aged mice with PBS or ɑ-syn pff injection. A Representative images of p-ɑ-syn immunostaining in young mouse cohort at 1-month post injection. Images are from three different mice (1, 2 and 3) of three brain regions (M1/M2 or somatosensory cortex (Neocortex), basolateral/basomedial amygdala (Amygdala), and dorsal striatum (Striatum)). Left panels are PBS (vehicle) injected and right are ɑ-syn pff injected. B Image analysis of p-ɑ-syn % area of neuropil of young mouse cohort at 1-month post injection. C p-ɑ-syn immunostaining of young mouse cohort at 3-months post injection. Same format as (A). D Image analysis of p-ɑ-syn % area of neuropil of young mouse cohort at 3-months post injection. E p-ɑ-syn immunostaining of aged mouse cohort at 1-month post injection. Same format as (A). F Image analysis of p-ɑ-syn % area of neuropil of aged mouse cohort at 1-month post injection. G p-ɑ-syn immunostaining of aged mouse cohort at 3-months post injection. Same format as (A). H Image analysis of p-ɑ-syn % area of neuropil of aged mouse cohort at 3-months post injection. I-K Comparison of image analysis of p-ɑ-syn positive % area of neuropil in neocortex (I), amygdala (J) and striatum (K) of ɑ-syn pff injected mice at 1- and 3-months post-injection in young (blue) and aged (red) mouse cohorts. Scale bars, 25 μm. Data are mean ± SEM. Unpaired t test was used. ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001