Figure 1.
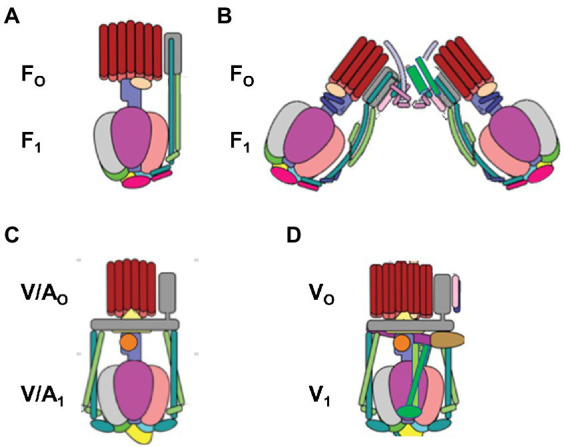
Structural variations among the family of rotary ATP synthases and ATPases that are coupled to transmembrane proton, or rarely sodium, gradients. (A) F-type ATP synthases in bacteria and plant chloroplasts (pdb-IDs 6OQR and 6FKF). (B) F-type ATP synthases in mitochondria (pdb-ID 6B8H). (C) V-type ATPases in some bacteria such as E. hirae and V/A-type ATP synthases in archaebacteria (pdb-ID 6R0Z) (D) V-type ATPases in vacuoles (pdb-ID 3J9V). V-type motors are incapable of synthesizing ATP and are used to pump protons to create a transmembrane pH gradient.
