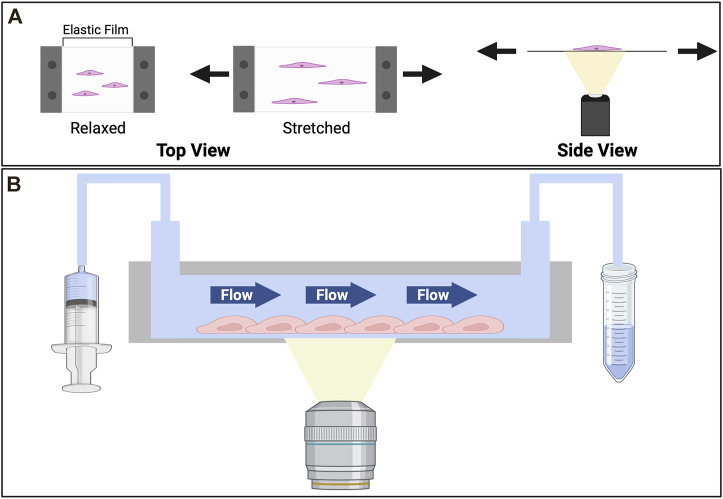
FIGURE 3.
Devices for in vitro studies of effects imposed by the tensile stress (stretch) and shear stress (flow). (A) Cell stretcher. To observe the effects of stretch cells are cultured on an elastic substrate which is mounted on a cell stretching device. The stretching device that reversibly deforms the elastic film. The stretcher itself is commonly mounted on an inverted microscope, where an objective underneath the elastic slide facilitates the imaging of dynamic cell behaviors upon stretching. To stretch the cells a prescribed strain is applied to the elastic substrate. (B) Microfluidic device. Consisting of a cell culture chamber with an inlet connecting to a syringe pump, and an outlet to collect the flow-through, the device can be used to study cellular responses to shear stress. Cells are seeded in the chamber. Medium is flown through at a prescribed rate. To collect images of cells over time, the device usually is mounted on an inverted microscope, where an objective is placed beneath the cell culture chamber.