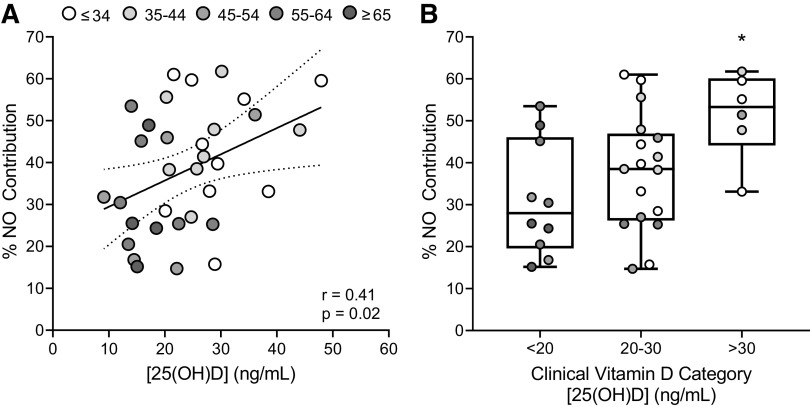
Figure 2.
A: association between serum vitamin D concentrations [25(OH)D] and the nitric oxide contribution (%NO) to the cutaneous vasodilation response to local heating (n = 33; 14 men, 19 women). Data were analyzed using simple linear regression analysis. Grayscale of individual data points indicates graded increases in M-index (AU), as shown in the legend. B: group comparisons in the %NO contribution to the local heating response when participants were separated into groups based on clinical vitamin D categories (deficient, <20 ng/mL; insufficient, 20–30 ng/mL; and sufficient, >30 ng/mL). Grayscale of individual data points indicates graded increases in M-index, as shown in the legend in A. Group comparisons were made using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc pairwise comparisons. *P < 0.05 compared with deficient.