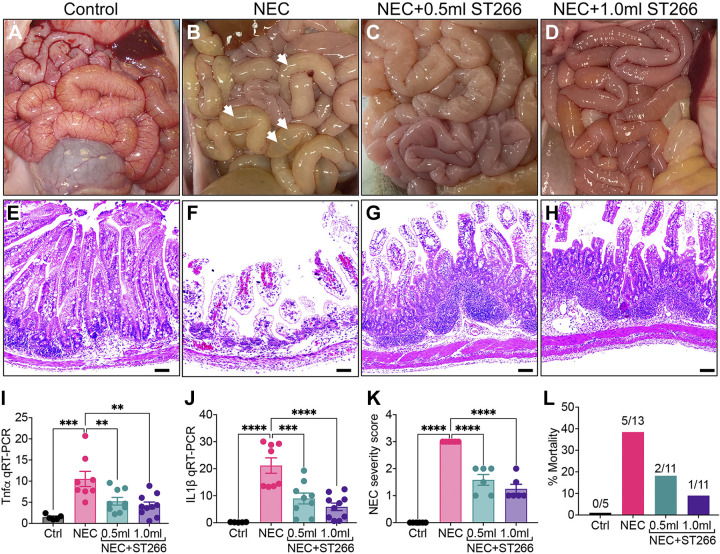
Figure 3.
Administration of ST266 prevents development of NEC in premature piglets. Gross images of the small bowel of control (A), NEC (B), NEC piglets given 0.5-mL ST266 (C), and NEC piglets given 1.0-mL ST266 (D) via intraperitoneal route once daily at 10 AM on each day of the NEC model. Representative H&E-stained histological images showing the intestinal mucosa of the terminal ileum in control (E), NEC (F), NEC piglets given 0.5-mL ST266 (G), and NEC piglets given 1.0-mL ST266 (H). qRT-PCR expression of proinflammatory cytokines Tnfα (I) and IL1β (J) in the intestinal mucosa. NEC severity score (K) and percentage mortality rate (L) (n = 6 piglets/group). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons tests using GraphPad Prism 9 software. **P < 0.01, *** or ****P < 0.001. Each dot on the graph represents a different piglet. qPCR data were obtained from Ctrl (n = 5), NEC (n = 8), NEC + 0.5 mL ST266 (n = 9), and NEC + 1.0 mL ST266 (n = 10) piglets. Scale bars, 200 µm. H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; NEC, necrotizing enterocolitis.