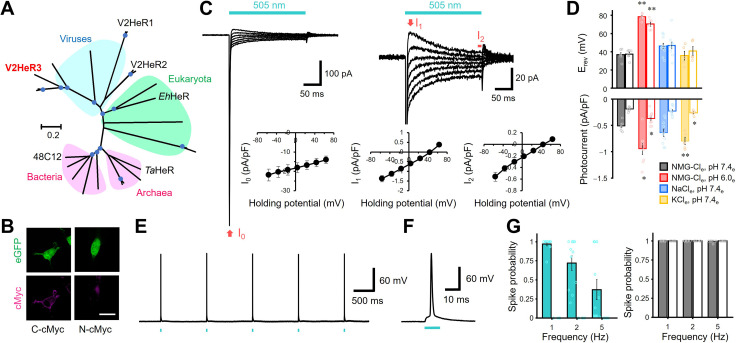
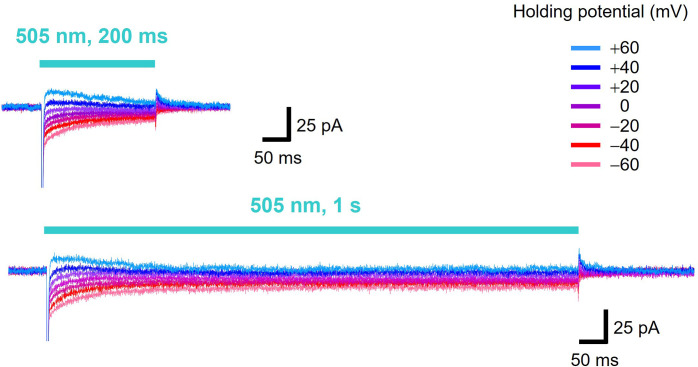
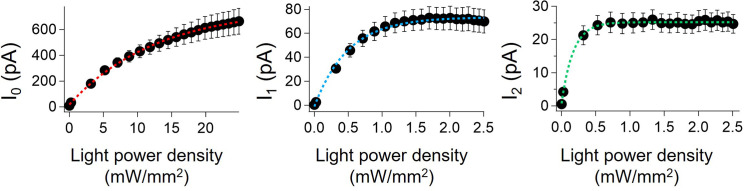
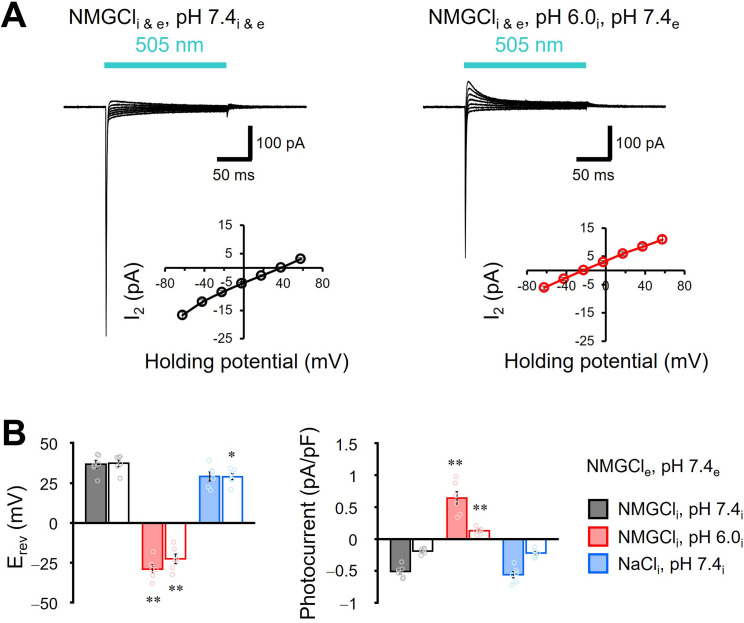
Figure 1. Light-gated inward proton transport of a viral heliorhodopsin (HeR) from Emiliania huxleyi virus 202 (V2HeR3).
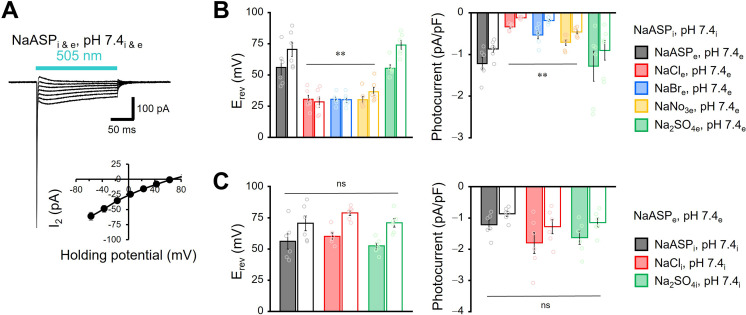
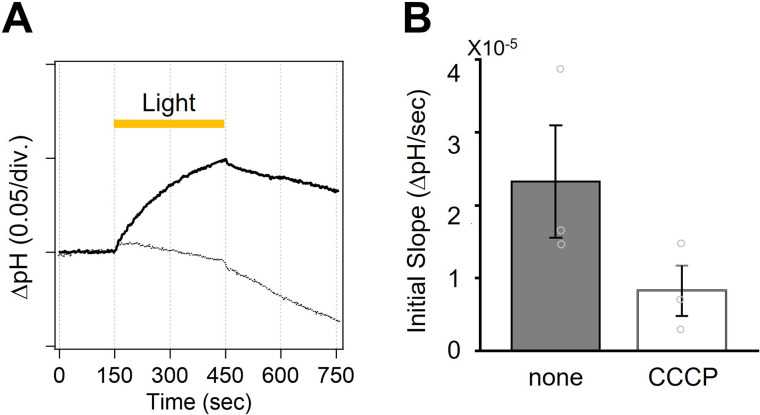
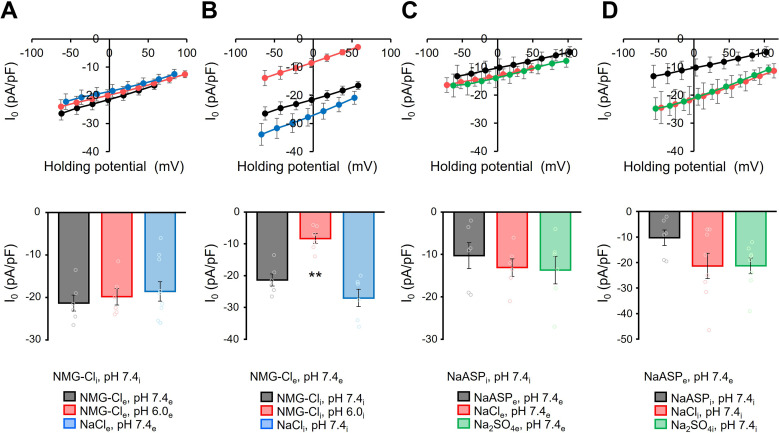
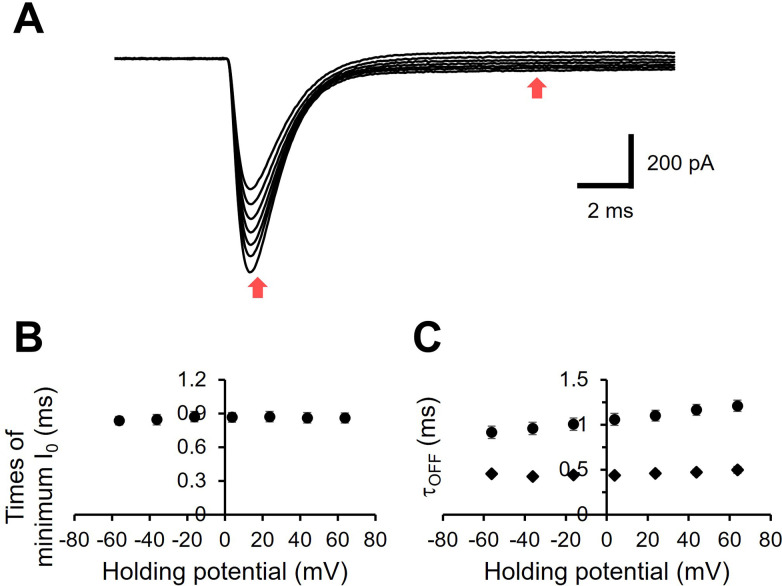
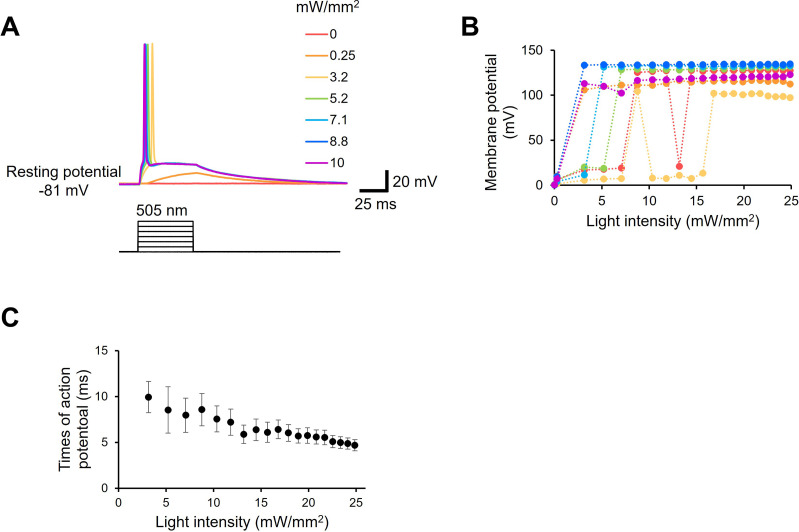
(A) Phylogenetic tree of HeRs, which includes three viral HeRs from E. huxleyi 202 (V2HeR1-3), a eukaryotic HeR from E. huxleyi (Ehux-HeR), an archaeal HeR (TaHeR) and a bacterial HeR (48C12). (B) eGFP fluorescence (top, green) and immunofluorescence staining (bottom, magenta) observation of V2HeR3 with a cMyc epitope tag at the C terminus (left) and the N terminus (right) in cultured ND7/23 cells. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Electrophysiological measurements of V2HeR3-driven photocurrent in ND7/23 cells. The cells were illuminated with light (λ=505 nm, 24.5 mW/mm2) during the time region shown by the blue bars. The membrane voltage was clamped from −60 to +60 mV for every 20 mV step. The pipette solution was 110 mM NMG-Cli, pH 7.4i, the bath solution was 140 mM NaCle, pH 7.4en=10 cells. (D) Corresponding reversal voltage (Erev) for each internal condition (upper), and comparison of photocurrent amplitudes at 0 mV for different internal cations (bottom). Square-block bar graph indicates Erev or amplitude from peak photocurrent (I1), open bar graphs indicate Erev or amplitude from steady-state photocurrent (I2). The pipette solution was 110 mM NMG-Cli, pH 7.4i, the bath solution was 140 mM NMG-Cle, pH 7.4e (black), 140 mM NMG-Cle, pH 6.0e (red), 140 mM NaCle, pH 7.4e (blue) or 140 mM KCle, pH 7.4e (yellow). n=5–10 cells. (*p<0.05, **p<0.01). (E) Representative responses of a V2HeR3-expressing neuron to 10 ms light pulses (left, λ=505 nm, 24.5 mW/mm2) at 1 Hz. (F) The firstaction potential in E. the X axis is expanded. (G) Comparison of spike probability by electrical stimulation (right, 300 pA current injections) or light stimulation (left, λ=505 nm, 24.5 mW/mm2). The Square-block bar indicates spike probability from V2HeR3-expressing neurons, the open bar indicates spike probability from the neurons without V2HeR3. n=6–11 cells.