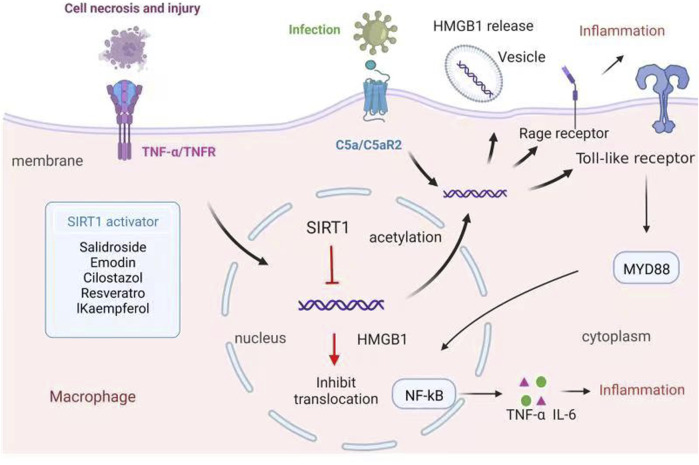
FIGURE 2.
Macrophage can be influenced by surrounding necrotic cells and promote the interaction between HMGB1 and its receptor RAGE mediated by TNF-α, releasing acetylated HMGB1 and enhancing inflammatory response. When macrophage is infected, C5a binding with its receptor C5aR2 induces upregulation of HMGB1 expression in cytosyl and transfer of HMGB1 from cytosyl to the cell membrane in the vesicle. HMGB1 in the cytoplasm can activate MyD88 through TLR and then activate downstream transcription factor NF-κB, make it transfer to the nucleus, and finally promote the release of TNF-α, IL-6 and other inflammatory factors. HMGB1, as a substrate of SIRT1, can be inhibited the release under the SIRT1 deacetylation, then improving inflammation. Thus, SIRT1 activators can be used as potential agents to control inflammation by increasing SIRT1 expression. HMGB1, High mobility group box 1; RAGE, the receptor for advanced glycation end-products; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; TLR, toll-like receptor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-6, interleukin-6.