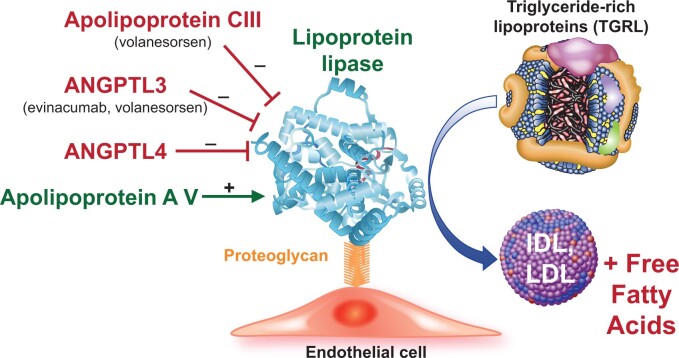
Figure 4.
Lipoprotein lipase modifiers. The enzyme lipoprotein lipase (depicted by the ribbon structure) associates with the surface of endothelial cells by binding to proteoglycans. This enzyme trims triglyceride from triglyceride-rich lipoproteins which include remnants of chylomicrons produced by intestinal cells from dietary lipid and very low-density lipoproteins synthesized endogenously by the liver. Lipoprotein lipase-mediated hydrolysis yields free fatty acids and low-density lipoprotein and intermediate-density lipoproteins. The proteins named in red inhibit lipoprotein lipase, and thus raise blood triglyceride-rich lipoprotein concentrations by limiting triglyceride-rich lipoprotein catabolism. The novel therapeutic agents listed inhibit these inhibitors and thus lower triglyceride-rich lipoprotein levels. Apolipoprotein AV activates lipoprotein lipase (shown in green.) Very strong human genetic evidence support the causality of each of the modulatory proteins depicted in regulating triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. ANGPTL, angiopoietin-like protein.