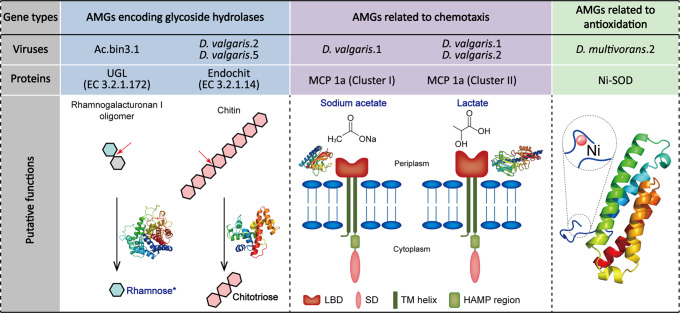
Fig. 4. Putative functions of proteins encoded by auxiliary metabolic genes (AMGs) of viruses infecting SRMs.
UGL D-4,5-unsaturated β-glucuronyl hydrolase, Endochit endochitinase, MCP methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein, Ni-SOD nickel-containing superoxide dismutase, LBD ligand-binding domain, SD signaling domain, TM transmembrane, HAMP histidine kinase, adenyl cyclase, methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein and phosphatase. Representative substrates of glycoside hydrolases (GHs) encoded by AMGs and the associated simplest products are shown. The cleavage points of the substrates are indicated by red arrows. The computational protein models of GHs, MCPs and Ni-SOD are displayed. Representative ligands of MCPs and the active site of Ni-SOD are shown. *, if the products of GHs or representative ligands of MCPs can be utilized directly by SRMs to reduce sulfate, their names are in blue. Additional details are presented in Supplementary Tables 10 and 11.