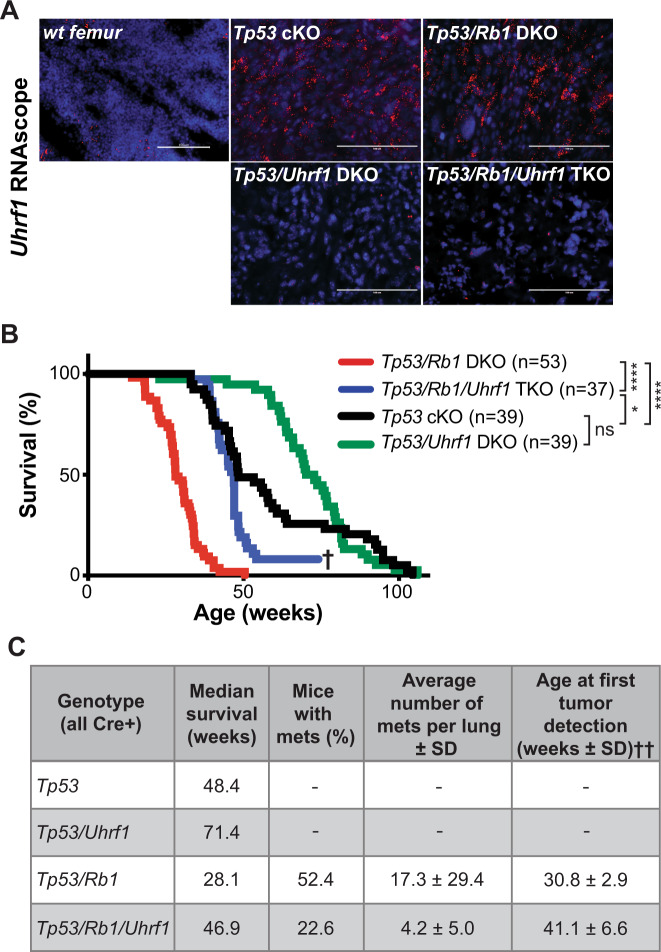
Fig. 6. UHRF1 is a critical driver of the increased malignancy observed in RB-null osteosarcoma.
A Representative fluorescent images of in situ hybridizations using RNAscope on wild-type femurs or tumors from genetically engineered osteosarcoma mice using a probe against Uhrf1 (red). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Uhrf1 expression is detected in Tp53 cKO and Tp53/Rb1 DKO mouse tumors but is low or not detected in wt, Tp53/Uhrf1 DKO, and Tp53/Rb1/Uhrf1 TKO tumors. B Kaplan–Meier curves showing the survival of osteosarcoma mouse models. Mice bearing Rb1 mutations Tp53/Rb1 DKO: Osx-Cre; p53lox/lox; Rb1lox/lox (red; n = 53) have significantly shorter lifespan compared to Tp53 cKO: Osx-Cre; p53lox/lox; Rb1lox/lox (black; n = 39). This survival time was significantly increased in Tp53/Rb1/Uhrf1 TKO: Osx-Cre; p53lox/lox; Rb1lox/lox; Uhrf1lox/lox (blue; n = 37) mice. †Three surviving mice were removed from the study to confirm tumor absence. Tp53/Uhrf1 DKO: Osx-Cre; p53lox/lox; Uhrf1lox/lox (green; n = 39) showed an overall survival comparable to Tp53 cKO (black; n = 39). Mantel–Cox test were used for curve comparisons. ns not significant, *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001. C Summary table for each osteosarcoma mouse model. ††Age of mice (weeks) at earliest tumor detection via microCT and PET scans comparison: P < 0.05 by unpaired two-tailed t test; Tp53/Rb1 DKO (n = 4) and Tp53/Rb1/Uhrf1 TKO (n = 3).