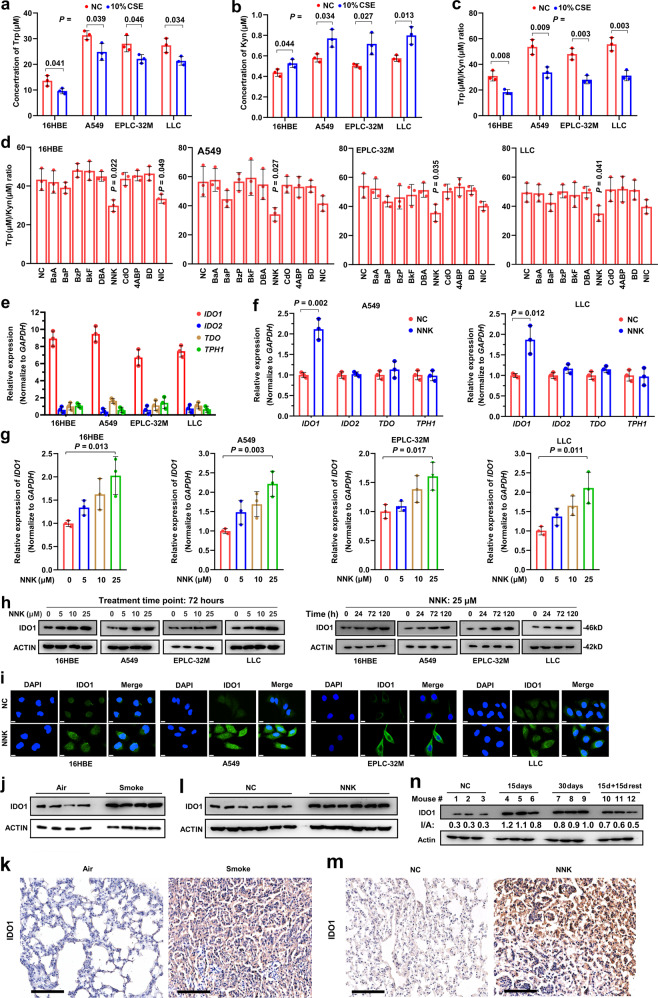
Fig. 2.
NNK causes the imbalance of Trp/Kyn through IDO1. a–c Trp concentration (a), Kyn concentration (b), and Trp/Kyn ratio (c) in supernatants of 16HBE, A549, EPLC-32M, and LLC cells treated with 10% cigarette smoke extract (CSE) for 72 h. d Trp/Kyn ratio in supernatants of 16HBE, A549, EPLC-32M, and LLC cells treated with ten tobacco compounds at 25 μM for 72 h. e The expression of four Trp-metabolizing enzymes in the cells. f The changes in the expression of Trp-metabolizing enzymes in A549 and LLC cells after treatment with NNK at 25 μM for 72 h. g IDO1 expression in the cells treated with NNK at indicated concentrations for 72 h was detected by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). h The cells were treated with NNK at indicated protocols, lysed, and subjected to western blot assays. i IDO1 expression in the cells treated with NNK at 25 μM for 72 h was detected by immunofluorescence assays. j, k The A/J mice were exposed to tobacco smoke for 180 days and sacrificed, and lung tissues were subjected to western blot (j) and immunohistochemistry (k) assays to detect the expression of IDO1. Scale bar = 100 μm. l, m The A/J mice were treated with NNK at 50 mg/kg/day for 90 days and sacrificed, and IDO1 expression in lung tissues was detected by western blot (l) and immunohistochemistry (m). Scale bar = 100 μm. n The A/J mice were treated with NNK for 15 to 30 days, or treated with NNK for 15 day and then stopped treatment for additional 15 days, sacrificed, and IDO1 expression in lung tissues was detected by western blot. P values, Student’s t test. Error bars, sd