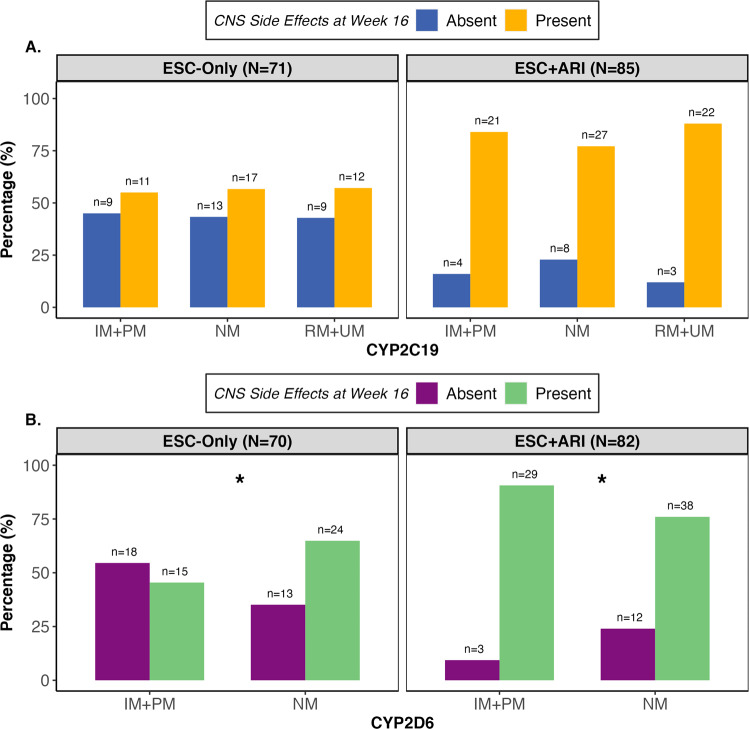
Fig. 3. Central nervous system (CNS) side effects self-reported to be present or absent by CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 metabolizer groups and treatment arm.
A Central Nervous System (CNS) side effects did not show an association with CYP2C19 metabolizer group. B Presence of CNS side effects was influenced by CYP2D6 metabolizer group. In ESC-Only, the odds of reporting a CNS side effect was 7.69 (SE = 6.09, 95% CI 1.63, 36.30) times higher for NMs compared to IM + PMs (χ2 (1, N = 70) = 6.65, p = 0.010, q = 0.048). The ESC + ARI treatment arm also showed an association between CNS side effects and CYP2D6 metabolizer group (χ2 (1, N = 82) = 6.70, p = 0.010, q = 0.049). The odds of reporting a CNS side effect 11.52 (SE = 10.90, 95% CI 1.80, 73.35) times higher for IM + PMs compared to NMs in this treatment arm. All logistic regression analyses were adjusted for age, ancestry, sex, recruitment site, total MADRS score at baseline, CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 metabolizer groups. P-values are corrected for multiple testing using the false discovery rate (FDR) approach. ARI aripiprazole, ESC escitalopram, IM intermediate metabolizer, NM normal metabolizer, PM poor metabolizer, RM rapid metabolizer, UM ultra-rapid metabolizer. *q < 0.05.