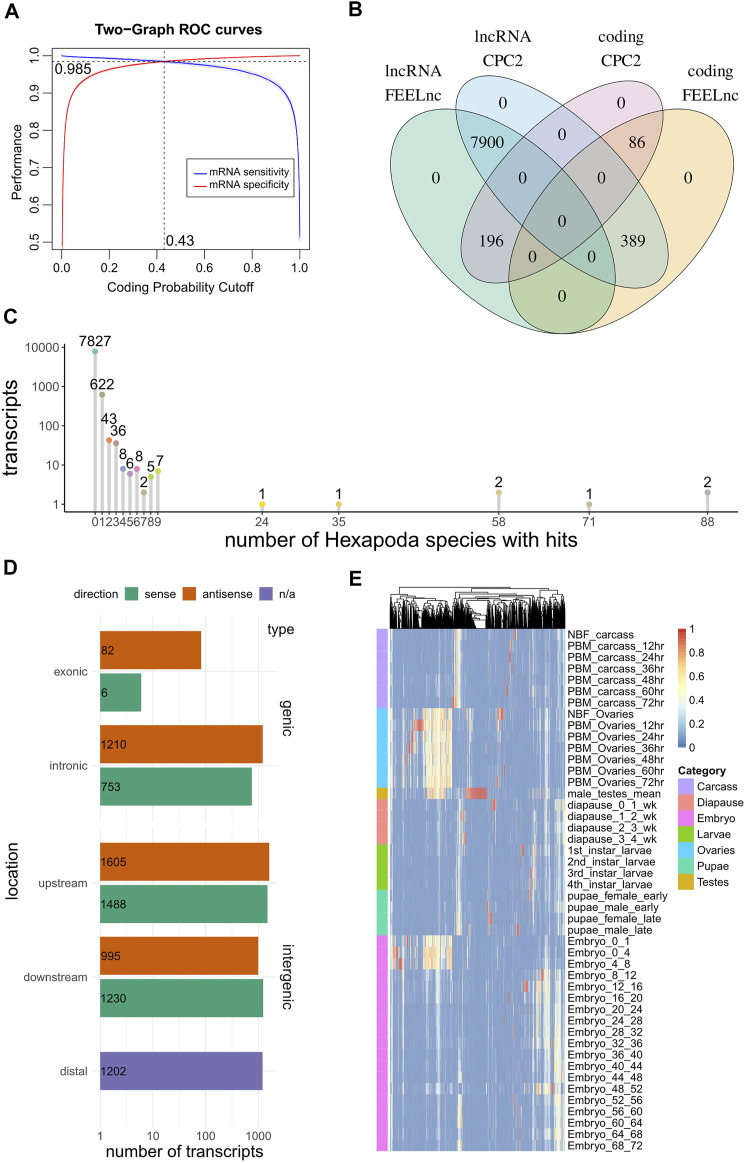
FIGURE 1.
Computational analysis of RNAs predicted to be non-coding via automated NCBI analysis. (A) A coding potential prediction model (FEELnc Random Forests) was trained specifically on Ae. albopictus sequences. The optimal cutoff to discriminate coding from non-coding sequences was set at the point where sensitivity and specificity was maximized (10-fold cross validation). (B) Overlap of coding potential predictions between FEELnc and CPC2 models. (C) Depiction of number of transcripts presenting hits to other Hexapoda species. Transcripts are tallied by the number of species in which they presented BLASTn hits (x-axis). (D) Genomic localization of lncRNAs, per type (genic/intergenic), subcategory (exonic/intronic/upstream/downstream/distal (i.e., >100 kb afar from other transcripts) and strand relative to close/overlapping elements (sense/antisense). (E) Heatmap of per-context fractions for all lncRNAs presenting tau > 0.5.