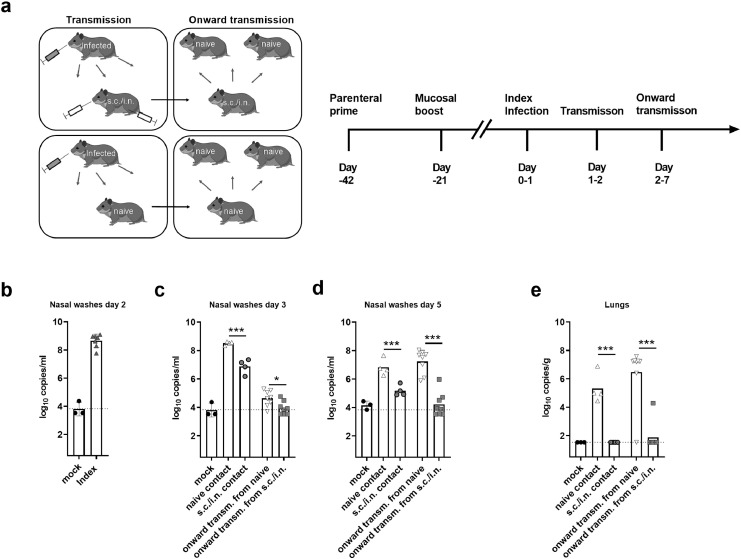
Figure 4.
Syrian hamsters were vaccinated with spike HexaPro trimer protein formulated in cationic liposomes (CAF®01) via subcutaneous priming – intranasal boost (s.c./i.n) or left unvaccinated (naïve). The hamsters were then housed with index animals, which had been challenged intranasally with 1.8 × 105 TCID50 of SARS-CoV-2 24 h earlier. Virus transmission was allowed to occur for 24 h. The vaccinated and unvaccinated hamsters were then co-housed for five days with another set of naïve animals to monitor onward transmission. a) Schematic of the study setup. b) Viral load in nasal washes of index animals at two days post infection (dpi) measured by a diagnostic qPCR against the E-gene c) Viral load in nasal washes of contact animals measured at 3 dpi and d) 5 dpi measured by a diagnostic qPCR against the E-gene. e) Viral load in lungs at 7 dpi. The stippled lines indicate the limit of detection. Bars indicate mean. Figures represent n= three (mock), four (index and vaccinated) or eight (onward contacts) hamsters per group. There was no statistically significance among groups if not otherwise indicated. Statistically significant differences are indicated by *** (Student t-test, p<0.01). Created with BioRender.com.