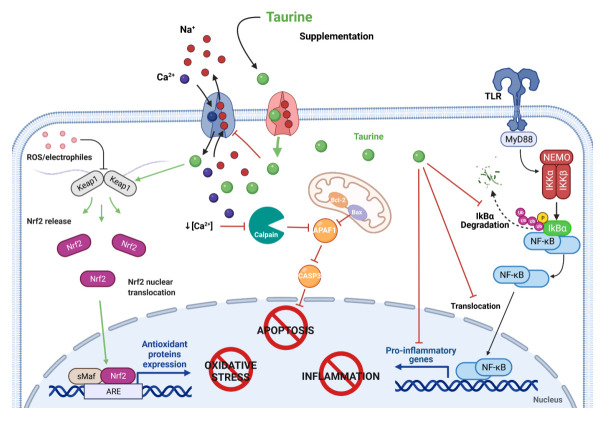
Fig. 3.
Cytoprotective roles of taurine against cell damage. Antioxidant activity: taurine facilitates the release of the nuclear factor E2-related factor (Nrf2), a redox-sensitive transcription factor, by the Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), and the translocation of Nrf2 to the nucleus and its binding to the antioxidant response element (ARE) activates the gene transcription of antioxidant enzymes. Anti-apoptotic activity: taurine’s contribution to calcium homeostasis blocks the activation of the calpain-dependent apoptotic cascade. Anti-inflammatory activity: taurine represses the degradation of the inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) alpha (IκBα) and keeps NF-κB inactivated; it also prevents its translocation to the nucleus and reduces the transcription of genes encoding proinflammatory cytokines (created with BioRender.com). APAF1, apoptosis protease-activating factor-1; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; BCl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; CASP3, caspase-3; Ikβα, nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; MyD88, innate immune signal transduction adaptor; Nrf2, NEMO, NF-kappa-B essential modulator; sMaF, musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma; TLR, Toll-like receptor.