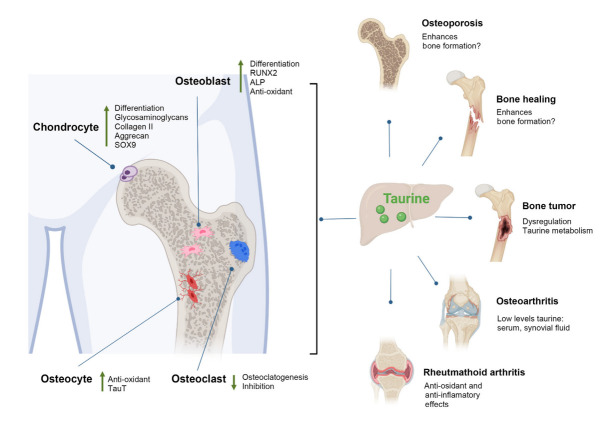
Fig. 4.
Potential actions of taurine in bone and cartilage. Taurine promotes osteogenesis by upregulating Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), as well as increasing alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and calcium deposition by osteoblasts; it also plays an antioxidant role in osteoblasts and osteocytes. In osteoclastogenesis, taurine exerts an inhibitory function. In chondrogenic differentiation, taurine promotes the synthesis of extracellular matrix components such as glycosaminoglycans and collagen, in addition to increasing the expression of SRY-box transcription factor 9 (SOX9). In bone and cartilage health, taurine promotes the formation of bone calluses in the consolidation process and promotes osseointegration. In pathological conditions such as osteoporosis, taurine supplementation increases bone mass, while in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and some bone tumors there are alterations in the metabolism of taurine (created with BioRender.com). TauT, taurine transporter.