FIGURE 2.
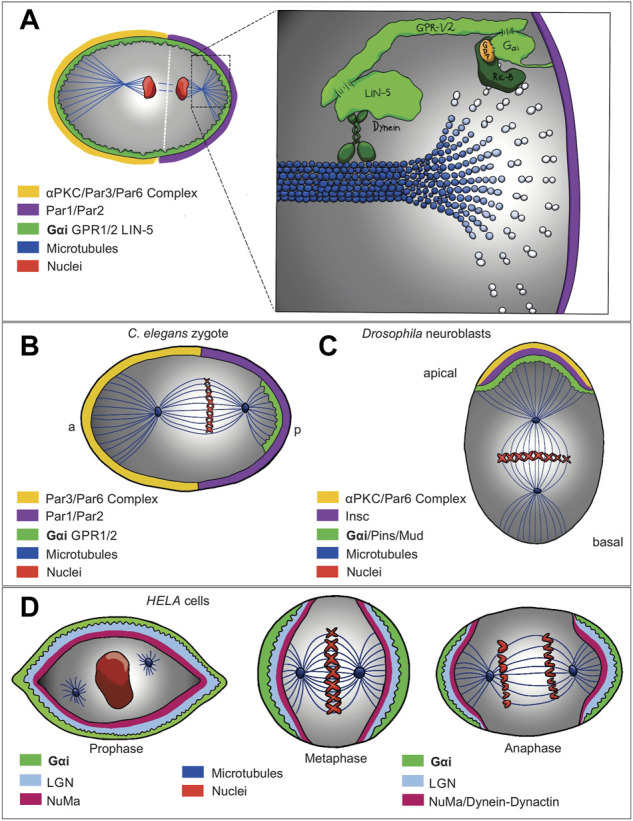
Gαi non-canonical signaling network models that show regulation of asymmetric cell division (A) in (C) elegans (B), Drosophila neuroblast (C) and HELA cells (D). Evolutionary conservation of a molecular complex composed of the Gαi subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein, LGN, dynein/dynactin complex and NuMA (respectively Gαi, Pins, and Mud in Drosophila, and GOA-1/GPA-16, GPR-1/2, and LIN5 in C. elegans) is localized at subcortical domain recruiting dynein, a motor protein, which also determines the movement along astral microtubules and generates pulling forces to orientate the spindle correctly. While Ric-8, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor, stimulates the exchange of GDP for GTP on the Gαi, triggering the dissociation of the complex that later, RGS activity stimulate the hydrolysis of GTP on Gαi, resulting in the Gαi-GDP reforming the Gαi-GDP/GPR-1/2 complex. On the other hand, Ric-8 as a scaffold protein, is required to localize Gαi and GPR-1/2 at the plasma membrane.
