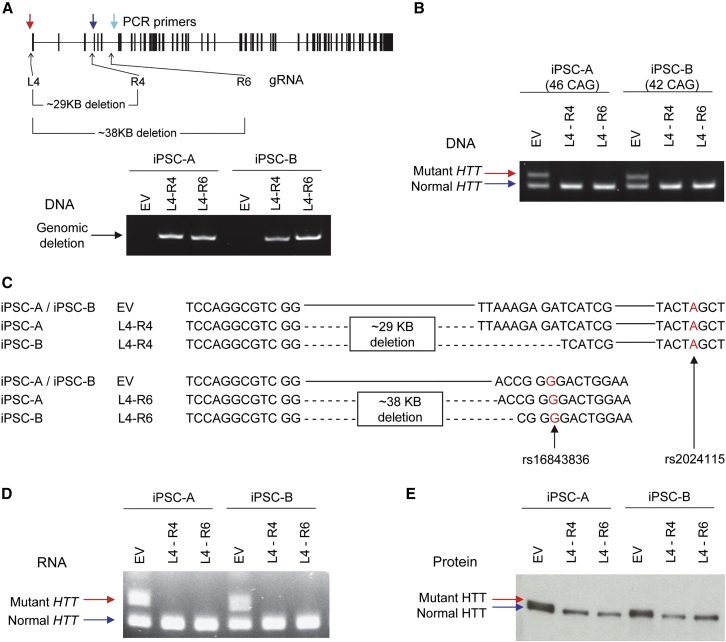
Figure 2.
Molecular consequences of allele-specific TP-CRISPR
To unequivocally determine the molecular consequences of allele-specific TP-CRISPR, we treated two independent HD iPSC lines (iPSC-A and iPSC-B) with either empty vector (EV) or a gRNA combination (L4-R4 or L4-R6) and established targeted clonal lines for subsequent analyses. (A) All EV-treated or targeted clonal lines were checked by PCR assays that were designed to detect a large genomic deletion using primers (colored arrows) that are described in the Materials and methods to confirm the presence of a genomic deletion in the targeted clonal lines. A schematic diagram on the top panel summarizes the locations for allele-specific target sites (L4, R4, and R6) and primers (colored arrows) with the sizes of predicted genomic deletion. The bottom panel shows representative data, displaying PCR products of 653 and 645 BP, which indicate genomic deletion by L4-R4 and L4-R6, respectively. EV, empty vector; L4-R4, TP-CRISPR using a gRNA combination L4 and R4; L4-R6, TP-CRISPR using a gRNA combination L4 and R6. (B) The presence and absence of expanded CAG repeat in the genomic DNA were determined by the PCR assays. Top (red arrow) and bottom bands (blue arrow) represent mutant and normal HTT, respectively. (C) To determine the sequence of targeted clonal lines, we performed Sanger sequencing. Since genomic deletion by L4-R4 (designed to excise ∼29 kb) involved both rs2857935 (L4) and rs16843804 (R4), assigning the deletion alleles to the mutant HTT was based on a downstream SNP rs2024115, whose “A” is on the hap.01 mutant haplotype. For L4-R6 combination, which was expected to excise ∼38 kb from the mutant HTT, we confirmed the genomic deletion on the mutant HTT based on the “G” allele at rs16843836. Contiguous and dotted lines represent unmodified DNA sequence and deletion, respectively. (D) We also performed RT-PCR assays to detect expanded and normal CAG repeats in the RNA samples. Top (red arrow) and bottom bands (blue arrow) represent mutant and normal HTT RNA, respectively. (E) Whole-cell lysate was resolved by SDS-PAGE and probed by MAB2166 for immunoblot analysis of HTT protein. Top (red arrow) and bottom (blue arrow) bands represent mutant and normal huntingtin protein, respectively. Note, since adult-onset CAG repeats do not increase the size of huntingtin protein substantially, separation of full-length mutant and normal HTT protein on the gel is usually incomplete.