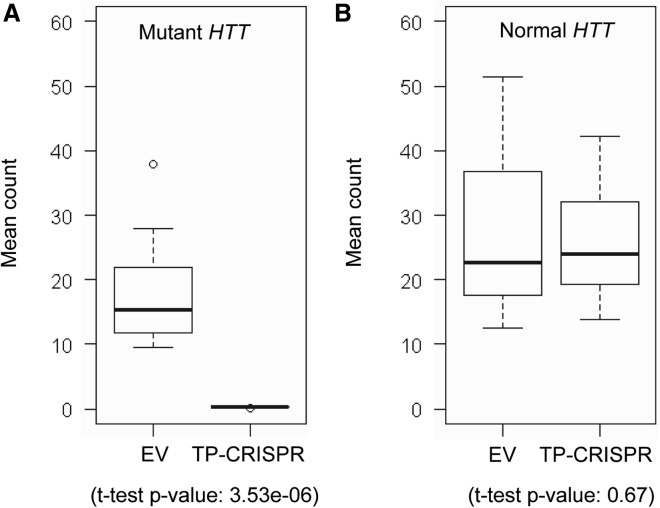
Figure 3.
High levels of mutant HTT specificity supported by RNA-seq analysis
Allele-specific expression (ASE) analysis was performed to evaluate the levels of allele specificity of our TP-CRISPR strategies. HD subjects with the most frequent diplotype (i.e., hap.01 and hap.08) are heterozygous at 10 exonic SNPs. Thus, we performed ASE using those 10 exonic SNP sites. Alleles of those 10 exonic SNPs on the mutant and normal HTT were based on our haplotype definitions and previous sequencing analysis. We counted the alleles on the mutant and normal HTT for a given SNP site, and then calculated average values. (A) Mean allele counts of 10 heterozygous exonic SNPs on the mutant HTT are summarized. Boxes on the left and right represent the distribution of alleles on the mutant HTT in EV-treated and targeted clonal lines, respectively. Student’s t test was performed (nominal p value, 3.53e−6). (B) The same analysis approach was applied to alleles of 10 heterozygous exonic SNPs that are on the normal HTT. Boxes on the left and right represent the distribution of alleles in EV-treated and targeted clonal lines, respectively. Student’s t test was performed (nominal p value, 0.67). Each box shows maximum, 75%, 50% (median), 75% quartile, and minimum.