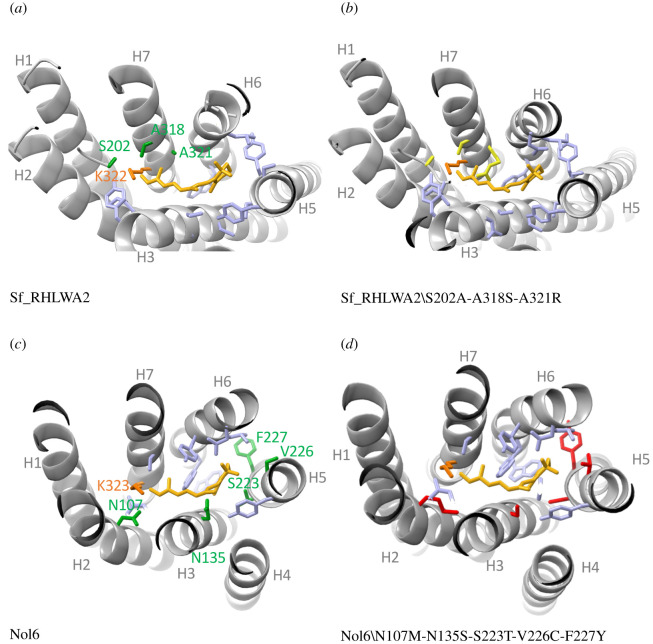
Figure 3.
Example of homology modelling to identify tuning sites among duplicate LW Gq opsins. (a) Structure of the dragonfly Sympetrum frequens Sf_RhLWA2 opsin built against homology modelling with the jumping spider crystal structure (PDB 6i9k). Among 127 variant sites with Sf_RhLWD1, three variant sites are within 5 Å of the cis-retinal chromophore. Helices are represented in light grey, the cis-retinal is represented in yellow, residues predicted to interact with the chromophore are in light blue (electronic supplementary material, dataset S3). Among these, the three variant candidate spectral sites are coloured in green. (b) Sf_RhLWA2 structure with the three variant sites mutated to those of Sf_RhLWD1 and coloured in yellow. (c) Structure of the green-sensitive NoL6 LW Gq opsin of the stomatopod Neogonodactylus oerstedii modelled against 6i9k. Among 155 variant sites with the red-shifted sensitive NoL14 opsin, five candidate spectral sites, coloured in green, are found in the vicinity of the chromophore. (d) NoL6 structure with mutated residues corresponding to NoL14 at each candidate spectral site. The templates and models were built in SwissModel followed by visualization in PyMol.