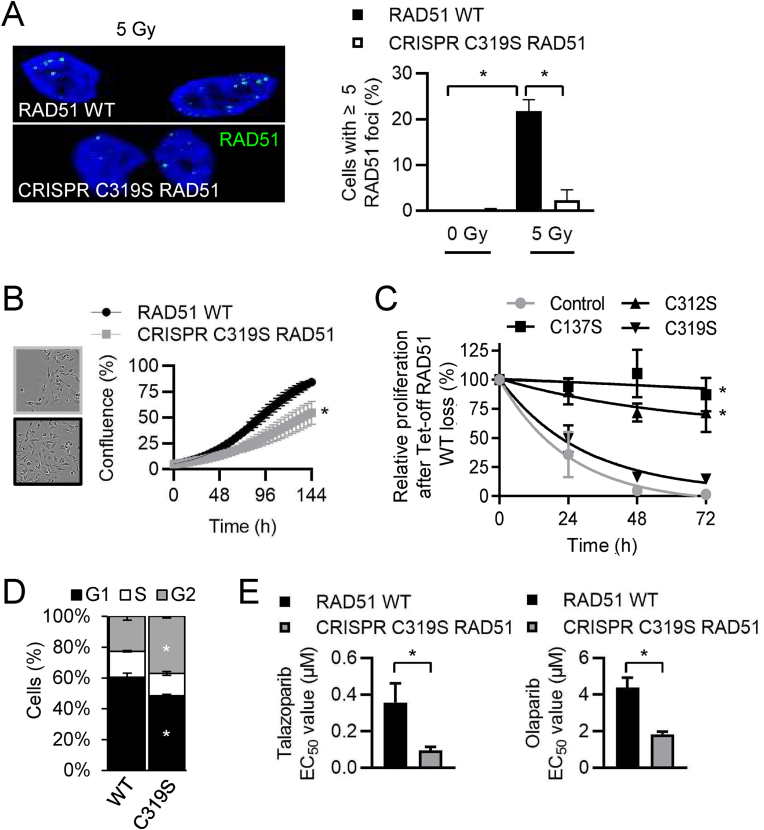
Fig. 2.
Cys319Ser RAD51 cells exhibit diminished IR-induced RAD51 foci formation and proliferation and increased sensitivity to PARP inhibitors.
(A) CRISPR/Cas-9 mutated homozygous Cys319Ser MM231 cells have decreased RAD51 foci formation (green) following IR with 5 Gy. DAPI stained nuclei (blue) merged images are shown. Cells plated on coverslips were dosed with 5 Gy then processed for IF after 5 h. Mean percentages of RAD51 WT (black) or RAD51 Cys319Ser (gray) cells with 5 or more foci from confocal z-stacked images dosed with 0 or 5 Gy + SEM from 3 independent experiments are shown.
(B) Proliferation of MM231 cells harboring RAD51 WT (black) or homozygous CRISPR/Cas-9 mutated Cys319Ser RAD51 (gray) was measured using the Incucyte ZOOM automated microscope to determine the percent confluence of phase contrast images over 144 h.
(C) Relative cell proliferation following doxycycline induced inhibition of conditionally Rad51 null DT40 cells. Doxycycline inhibits WT RAD51 (●) and leaves only transgenic expression of RAD51C319S (▼), C137S (■) or C312S (▲) mutants as indicated. Curve shows mean cell percentage difference ± SEM of the relative cell number in the presence and absence of the Tet-controlled transgene.
(D) Cell cycle analysis of propidium iodide stained RAD51 WT MM231 or CRISPR Cys319Ser RAD51 mutated cells was performed by flow cytometry. Mean ± SEM, n = 3 (E) Dose response assays (6-points, 0–50 μM) were performed with talazoparib or olaparib over 7-days and EC50 values are indicated as mean ± SEM, n = 3. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)