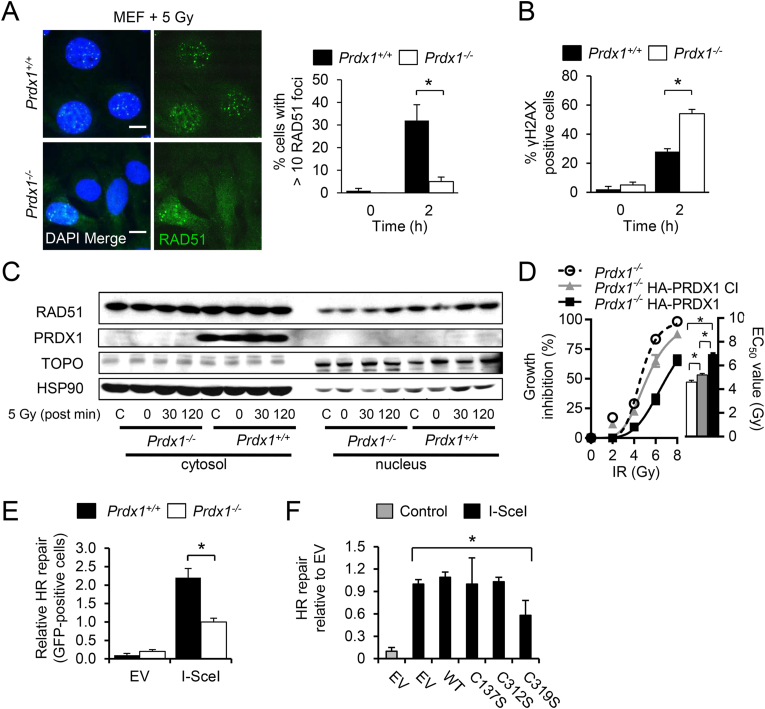
Fig. 5.
PRDX1-deficiency sensitizes cells to IR and inhibits both HR and RAD51 foci formation.
(A) IF images of Prdx1+/+ or Prdx1−/− MEFs stained with RAD51 antibody post-IR with 5 Gy. Scale bar indicates 10 μm. PRDX1 deficiency decreased RAD51 foci formation when challenged with IR. Prdx1+/+ (black bars) or Prdx1−/− (white bars) MEFs underwent IR with 0 or 5 Gy and RAD51 foci were counted after 2 h. Values represent cells with more than 10 RAD51 foci per cell.
(B) PRDX1 deficiency increased ɣH2AX foci formation when challenged with IR. Prdx1+/+ (black bars) or Prdx1−/− (white bars) MEFs underwent IR with 0 or 5 Gy and ɣH2AX positive cells were measured after 2 h.
(C) Immunoblots of cell fractionation lysates of Prdx1+/+ or Prdx1−/− MEFs following 0 or 5 Gy with post-IR time points from 0 to 120 min.
(D) Loss of PRDX1 activity inhibited clonogenic growth with increasing ɣ-irradiation (IR). Prdx1−/− MEFs were reconstituted with empty vector (ㅇ) or HA tagged wild-type (■) or catalytically inactive PRDX1 ( ). EC50 values indicate mean + SEM, n = 3.
). EC50 values indicate mean + SEM, n = 3.
(E) Loss of PRDX1 activity decreased homologous recombination when DNA double strand breaks were induced in MEFs. Prdx1+/+ (black bars) or Prdx1−/− (white bars) MEFs were infected with a DR-GFP expression vector and the recombined GFP signal was measured in the presence or absence of I-SceI.
(F) DR-GFP assay shows the relative HR in Prdx1−/− MEFs transduced with WT or cysteine mutant RAD51 constructs transfected with I-SceI.