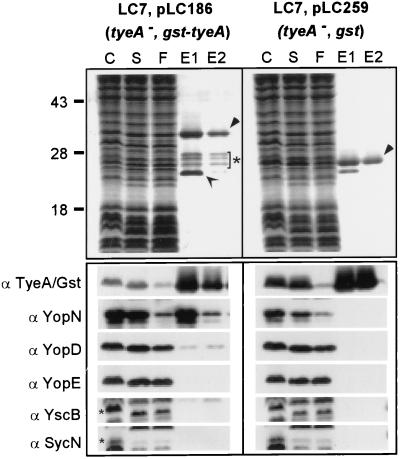
FIG. 6.
Binding of Gst-TyeA to YopN and YopD. Y. enterocolitica LC7(pLC199) and Y. enterocolitica LC7(pLC100) were grown at 37°C and induced for type III secretion by the chelation of calcium ions. Expression of the Gst and the Gst-TyeA proteins was induced by the addition of 1 mM IPTG to the culture medium. Cells (1012 CFU) were harvested by centrifugation, suspended in buffer, and lysed in a French pressure cell to generate the crude extract (C). Unbroken cells were removed by centrifugation at 6,000 × g. Membranes were sedimented by ultracentrifugation at 100,000 × g, and the supernatant (S), containing soluble cytosolic contents, was subjected to affinity chromatography on glutathione-Sepharose. Flowthrough (F) and eluate (E) fractions after the addition of 10 mM glutathione were collected and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining. The migrations of full-length Gst-TyeA and Gst are marked by filled arrowheads. Gst-TyeA species within the bracket marked with a star represent degradation products that were observed in large-scale purifications but not during immunoblotting of TCA-precipitated cultures. The open arrow represents an unknown glutathione-Sepharose binding protein of Y. enterocolitica. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with antisera raised against Gst-TyeA, YopN, YopD, YopB, YscB, and SycN. YopN and YopD copurified with Gst-TyeA but not with Gst. Small star, migration of YscB and SycN on an SDS-PAGE gel.